You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000000105_01150
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000000105_01150
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Bacteroides clarus | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; Bacteroides; Bacteroides clarus | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000000105_01150 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | PL1 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 286463; End: 288913 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL1 | 381 | 585 | 6.1e-62 | 0.9890710382513661 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd14948 | BACON | 5.29e-14 | 30 | 123 | 1 | 82 | Bacteroidetes-Associated Carbohydrate-binding (putative) Often N-terminal (BACON) domain. The BACON domain is found in diverse domain architectures and accociated with a wide variety of domains, including carbohydrate-active enzymes and proteases. It was named for its suggested function of carbohydrate binding; the latter was inferred from domain architectures, sequence conservation, and phyletic distribution. However, recent experimental data suggest that its primary function in Bacteroides ovatus endo-xyloglucanase BoGH5A is to distance the catalytic module from the cell surface and confer additional mobility to the catalytic domain for attack of the polysaccharide. No evidence for a direct role in carbohydrate binding could be found in that case. The large majority of BACON domains are found in Bacteroidetes. |
| cd14948 | BACON | 9.20e-06 | 227 | 305 | 4 | 82 | Bacteroidetes-Associated Carbohydrate-binding (putative) Often N-terminal (BACON) domain. The BACON domain is found in diverse domain architectures and accociated with a wide variety of domains, including carbohydrate-active enzymes and proteases. It was named for its suggested function of carbohydrate binding; the latter was inferred from domain architectures, sequence conservation, and phyletic distribution. However, recent experimental data suggest that its primary function in Bacteroides ovatus endo-xyloglucanase BoGH5A is to distance the catalytic module from the cell surface and confer additional mobility to the catalytic domain for attack of the polysaccharide. No evidence for a direct role in carbohydrate binding could be found in that case. The large majority of BACON domains are found in Bacteroidetes. |
| cd14948 | BACON | 3.48e-05 | 132 | 219 | 2 | 83 | Bacteroidetes-Associated Carbohydrate-binding (putative) Often N-terminal (BACON) domain. The BACON domain is found in diverse domain architectures and accociated with a wide variety of domains, including carbohydrate-active enzymes and proteases. It was named for its suggested function of carbohydrate binding; the latter was inferred from domain architectures, sequence conservation, and phyletic distribution. However, recent experimental data suggest that its primary function in Bacteroides ovatus endo-xyloglucanase BoGH5A is to distance the catalytic module from the cell surface and confer additional mobility to the catalytic domain for attack of the polysaccharide. No evidence for a direct role in carbohydrate binding could be found in that case. The large majority of BACON domains are found in Bacteroidetes. |
| smart00656 | Amb_all | 1.42e-04 | 396 | 570 | 17 | 173 | Amb_all domain. |
| pfam19190 | BACON_2 | 5.32e-04 | 31 | 115 | 2 | 84 | Viral BACON domain. This family represents a distinct class of BACON domains found in crAss-like phages, the most common viral family in the human gut, in which they are found in tail fiber genes. This suggests they may play a role in phage-host interactions. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QUT78065.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 816 | 1 | 795 |
| ALJ48967.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 816 | 1 | 795 |
| SCV08385.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 816 | 1 | 795 |
| QRQ55777.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 816 | 1 | 795 |
| QDM11683.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 816 | 1 | 795 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B8NQQ7 | 3.46e-37 | 322 | 799 | 21 | 414 | Probable pectate lyase C OS=Aspergillus flavus (strain ATCC 200026 / FGSC A1120 / IAM 13836 / NRRL 3357 / JCM 12722 / SRRC 167) OX=332952 GN=plyC PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q2UB83 | 1.16e-36 | 322 | 799 | 21 | 414 | Probable pectate lyase C OS=Aspergillus oryzae (strain ATCC 42149 / RIB 40) OX=510516 GN=plyC PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q0CLG7 | 3.91e-36 | 313 | 799 | 11 | 414 | Probable pectate lyase C OS=Aspergillus terreus (strain NIH 2624 / FGSC A1156) OX=341663 GN=plyC PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q5B297 | 1.00e-35 | 322 | 799 | 21 | 411 | Probable pectate lyase C OS=Emericella nidulans (strain FGSC A4 / ATCC 38163 / CBS 112.46 / NRRL 194 / M139) OX=227321 GN=plyC PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q4WL88 | 6.04e-35 | 317 | 799 | 16 | 415 | Probable pectate lyase C OS=Neosartorya fumigata (strain ATCC MYA-4609 / Af293 / CBS 101355 / FGSC A1100) OX=330879 GN=plyC PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
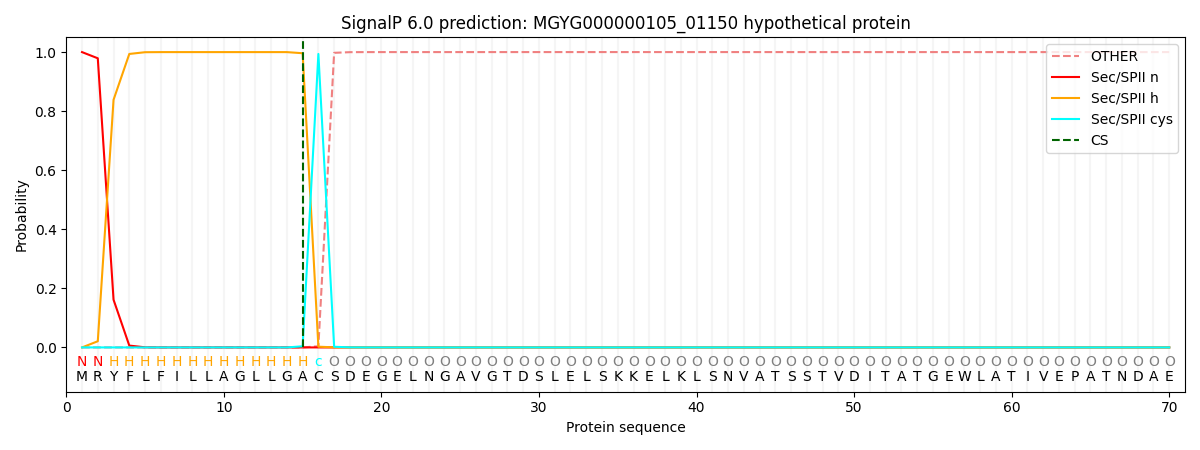
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 1.000019 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
