You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000001304_00203
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000001304_00203
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
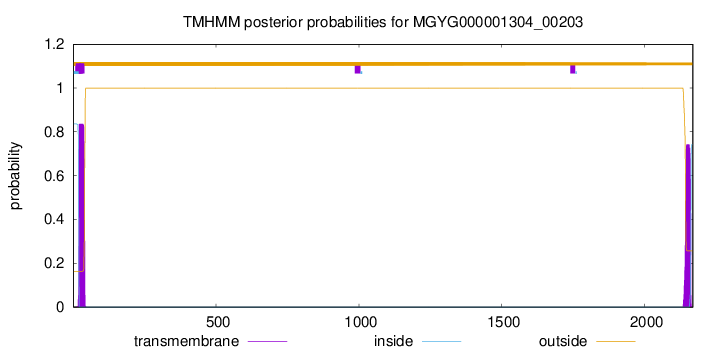
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Erysipelatoclostridium spiroforme | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Erysipelotrichales; Erysipelatoclostridiaceae; Erysipelatoclostridium; Erysipelatoclostridium spiroforme | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000001304_00203 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH31 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 247428; End: 253937 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH31 | 462 | 703 | 6.6e-57 | 0.5339578454332553 |
| CBM32 | 1699 | 1832 | 5.2e-25 | 0.9274193548387096 |
| CBM32 | 994 | 1120 | 6.2e-17 | 0.8951612903225806 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd06596 | GH31_CPE1046 | 0.0 | 294 | 674 | 1 | 334 | Clostridium CPE1046-like. CPE1046 is an uncharacterized Clostridium perfringens protein with a glycosyl hydrolase family 31 (GH31) domain. The domain architecture of CPE1046 and its orthologs includes a C-terminal fibronectin type 3 (FN3) domain and a coagulation factor 5/8 type C domain in addition to the GH31 domain. Enzymes of the GH31 family possess a wide range of different hydrolytic activities including alpha-glucosidase (glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase), alpha-xylosidase, 6-alpha-glucosyltransferase, 3-alpha-isomaltosyltransferase and alpha-1,4-glucan lyase. All GH31 enzymes cleave a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that varies considerably in size, depending on the enzyme, and may be either a starch or a glycoprotein. |
| pfam01055 | Glyco_hydro_31 | 1.30e-60 | 277 | 703 | 1 | 442 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 31. Glycosyl hydrolases are key enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism. Family 31 comprises of enzymes that are, or similar to, alpha- galactosidases. |
| COG1501 | YicI | 5.88e-59 | 56 | 810 | 4 | 772 | Alpha-glucosidase, glycosyl hydrolase family GH31 [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| cd08759 | Type_III_cohesin_like | 1.27e-41 | 1205 | 1369 | 1 | 166 | Cohesin domain, interaction partner of dockerin. Bacterial cohesin domains bind to a complementary protein domain named dockerin, and this interaction is required for the formation of the cellulosome, a cellulose-degrading complex. Two specific calcium-dependent interactions between cohesin and dockerin appear to be essential for cellulosome assembly, type I and type II. This subfamily represents type III cohesins and closely related domains. |
| cd06589 | GH31 | 3.30e-40 | 296 | 584 | 1 | 265 | glycosyl hydrolase family 31 (GH31). GH31 enzymes occur in prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and archaea with a wide range of hydrolytic activities, including alpha-glucosidase (glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase), alpha-xylosidase, 6-alpha-glucosyltransferase, 3-alpha-isomaltosyltransferase and alpha-1,4-glucan lyase. All GH31 enzymes cleave a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that varies considerably in size, depending on the enzyme, and may be either a starch or a glycoprotein. In most cases, the pyranose moiety recognized in subsite -1 of the substrate binding site is an alpha-D-glucose, though some GH31 family members show a preference for alpha-D-xylose. Several GH31 enzymes can accommodate both glucose and xylose and different levels of discrimination between the two have been observed. Most characterized GH31 enzymes are alpha-glucosidases. In mammals, GH31 members with alpha-glucosidase activity are implicated in at least three distinct biological processes. The lysosomal acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) is essential for glycogen degradation and a deficiency or malfunction of this enzyme causes glycogen storage disease II, also known as Pompe disease. In the endoplasmic reticulum, alpha-glucosidase II catalyzes the second step in the N-linked oligosaccharide processing pathway that constitutes part of the quality control system for glycoprotein folding and maturation. The intestinal enzymes sucrase-isomaltase (SI) and maltase-glucoamylase (MGAM) play key roles in the final stage of carbohydrate digestion, making alpha-glucosidase inhibitors useful in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. GH31 alpha-glycosidases are retaining enzymes that cleave their substrates via an acid/base-catalyzed, double-displacement mechanism involving a covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate. Two aspartic acid residues have been identified as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, respectively. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QIK85989.1 | 0.0 | 17 | 2115 | 3 | 2115 |
| QIK69254.1 | 0.0 | 54 | 2061 | 39 | 2000 |
| QJA02122.1 | 0.0 | 10 | 2071 | 1 | 2112 |
| BBK23937.1 | 0.0 | 10 | 2075 | 1 | 2088 |
| QBJ76643.1 | 0.0 | 26 | 2115 | 12 | 2070 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6M76_A | 1.33e-297 | 45 | 984 | 21 | 963 | GH31alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase from Enterococcus faecalis [Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 10100],6M77_A GH31 alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase from Enterococcus faecalis in complex with N-acetylgalactosamine [Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 10100] |
| 7F7R_A | 7.27e-297 | 45 | 984 | 21 | 963 | ChainA, GH31 alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase [Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 10100] |
| 7F7Q_A | 2.01e-296 | 45 | 984 | 21 | 963 | ChainA, GH31 alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase [Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 10100] |
| 4LKS_A | 1.41e-33 | 1703 | 1835 | 33 | 166 | Structureof CBM32-3 from a family 31 glycoside hydrolase from Clostridium perfringens in complex with galactose [Clostridium perfringens ATCC 13124],4LKS_C Structure of CBM32-3 from a family 31 glycoside hydrolase from Clostridium perfringens in complex with galactose [Clostridium perfringens ATCC 13124],4LQR_A Structure of CBM32-3 from a family 31 glycoside hydrolase from Clostridium perfringens [Clostridium perfringens ATCC 13124],4P5Y_A Structure of CBM32-3 from a family 31 glycoside hydrolase from Clostridium perfringens in complex with N-acetylgalactosamine [Clostridium perfringens ATCC 13124] |
| 6JR6_A | 3.34e-26 | 62 | 838 | 30 | 821 | Flavobacteriumjohnsoniae GH31 dextranase, FjDex31A [Flavobacterium johnsoniae UW101],6JR6_B Flavobacterium johnsoniae GH31 dextranase, FjDex31A [Flavobacterium johnsoniae UW101],6JR6_C Flavobacterium johnsoniae GH31 dextranase, FjDex31A [Flavobacterium johnsoniae UW101],6JR6_D Flavobacterium johnsoniae GH31 dextranase, FjDex31A [Flavobacterium johnsoniae UW101],6JR7_A Flavobacterium johnsoniae GH31 dextranase, FjDex31A, complexed with glucose [Flavobacterium johnsoniae UW101],6JR7_B Flavobacterium johnsoniae GH31 dextranase, FjDex31A, complexed with glucose [Flavobacterium johnsoniae UW101],6JR7_C Flavobacterium johnsoniae GH31 dextranase, FjDex31A, complexed with glucose [Flavobacterium johnsoniae UW101],6JR7_D Flavobacterium johnsoniae GH31 dextranase, FjDex31A, complexed with glucose [Flavobacterium johnsoniae UW101] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9F234 | 1.72e-32 | 195 | 812 | 144 | 775 | Alpha-glucosidase 2 OS=Bacillus thermoamyloliquefaciens OX=1425 PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q9FN05 | 8.28e-25 | 478 | 749 | 566 | 820 | Probable glucan 1,3-alpha-glucosidase OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=PSL5 PE=1 SV=1 |
| B9F676 | 2.46e-24 | 478 | 749 | 564 | 818 | Probable glucan 1,3-alpha-glucosidase OS=Oryza sativa subsp. japonica OX=39947 GN=Os03g0216600 PE=3 SV=1 |
| P79403 | 9.92e-24 | 469 | 749 | 585 | 851 | Neutral alpha-glucosidase AB OS=Sus scrofa OX=9823 GN=GANAB PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q14697 | 2.25e-23 | 469 | 749 | 585 | 851 | Neutral alpha-glucosidase AB OS=Homo sapiens OX=9606 GN=GANAB PE=1 SV=3 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
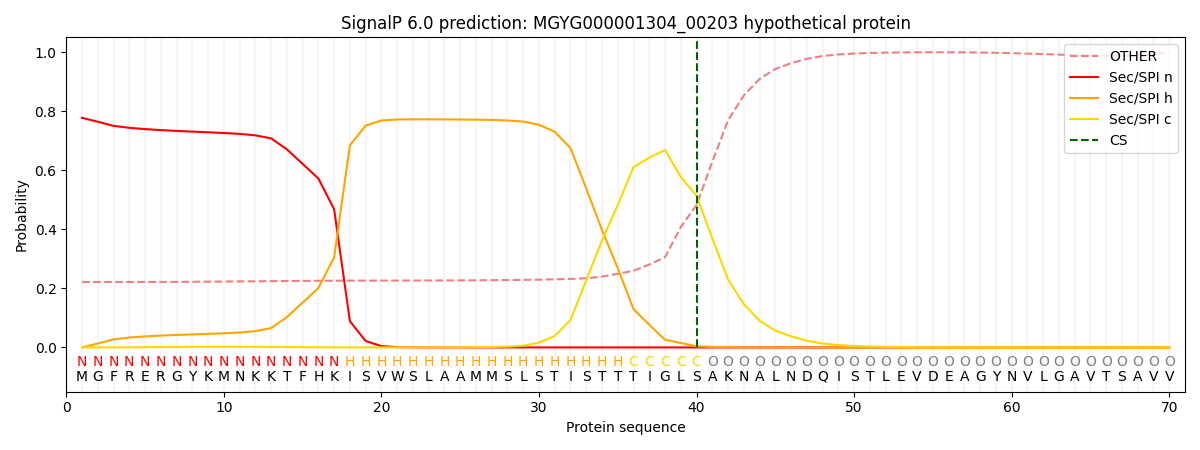
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.241350 | 0.752216 | 0.003309 | 0.001026 | 0.000705 | 0.001383 |