You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002048_00294
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002048_00294
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Collinsella sp002232035 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Actinobacteriota; Coriobacteriia; Coriobacteriales; Coriobacteriaceae; Collinsella; Collinsella sp002232035 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002048_00294 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM32 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 16394; End: 17437 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd14752 | GH31_N | 2.50e-20 | 164 | 278 | 10 | 122 | N-terminal domain of glycosyl hydrolase family 31 (GH31). This family is found N-terminal to the glycosyl-hydrolase domain of Glycoside hydrolase family 31 (GH31). GH31 includes the glycoside hydrolases alpha-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.20), alpha-1,3-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.84), alpha-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.177), sucrase-isomaltase (EC 3.2.1.48 and EC 3.2.1.10), as well as alpha-glucan lyase (EC 4.2.2.13). All GH31 enzymes cleave a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that varies considerably in size, depending on the enzyme, and may be either a starch or a glycoprotein. In most cases, the pyranose moiety recognized in subsite-1 of the substrate binding site is an alpha-D-glucose, though some GH31 family members show a preference for alpha-D-xylose. Several GH31 enzymes can accommodate both glucose and xylose and different levels of discrimination between the two have been observed. Most characterized GH31 enzymes are alpha-glucosidases. In mammals, GH31 members with alpha-glucosidase activity are implicated in at least three distinct biological processes. The lysosomal acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) is essential for glycogen degradation and a deficiency or malfunction of this enzyme causes glycogen storage disease II, also known as Pompe disease. In the endoplasmic reticulum, alpha-glucosidase II catalyzes the second step in the N-linked oligosaccharide processing pathway that constitutes part of the quality control system for glycoprotein folding and maturation. The intestinal enzymes sucrase-isomaltase (SI) and maltase-glucoamylase (MGAM) play key roles in the final stage of carbohydrate digestion, making alpha-glucosidase inhibitors useful in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. GH31 alpha-glycosidases are retaining enzymes that cleave their substrates via an acid/base-catalyzed, double-displacement mechanism involving a covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate. Two aspartic acid residues of the catalytic domain have been identified as the catalytic nucleophile and the acid/base, respectively. A loop of the N-terminal beta-sandwich domain is part of the active site pocket. |
| pfam16338 | DUF4968 | 2.15e-09 | 52 | 143 | 1 | 79 | Domain of unknown function (DUF4968). This family consists of uncharacterized proteins around 830 residues in length and is mainly found in various Bacteroides species. Several proteins in this family are annotated as alpha-glucosidases, but the function of this protein is unknown. |
| COG1501 | YicI | 1.18e-08 | 76 | 299 | 56 | 277 | Alpha-glucosidase, glycosyl hydrolase family GH31 [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| cd06596 | GH31_CPE1046 | 8.91e-08 | 276 | 307 | 1 | 32 | Clostridium CPE1046-like. CPE1046 is an uncharacterized Clostridium perfringens protein with a glycosyl hydrolase family 31 (GH31) domain. The domain architecture of CPE1046 and its orthologs includes a C-terminal fibronectin type 3 (FN3) domain and a coagulation factor 5/8 type C domain in addition to the GH31 domain. Enzymes of the GH31 family possess a wide range of different hydrolytic activities including alpha-glucosidase (glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase), alpha-xylosidase, 6-alpha-glucosyltransferase, 3-alpha-isomaltosyltransferase and alpha-1,4-glucan lyase. All GH31 enzymes cleave a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that varies considerably in size, depending on the enzyme, and may be either a starch or a glycoprotein. |
| PRK10658 | PRK10658 | 9.54e-08 | 111 | 305 | 89 | 275 | putative alpha-glucosidase; Provisional |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QOY60730.1 | 2.66e-118 | 32 | 330 | 46 | 346 |
| QWT17625.1 | 2.49e-102 | 17 | 314 | 21 | 327 |
| QUO30799.1 | 1.81e-96 | 49 | 335 | 35 | 321 |
| QNM10857.1 | 2.34e-93 | 46 | 311 | 50 | 314 |
| BBK61154.1 | 9.74e-90 | 18 | 329 | 18 | 339 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6M76_A | 1.46e-69 | 42 | 301 | 32 | 294 | GH31alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase from Enterococcus faecalis [Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 10100],6M77_A GH31 alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase from Enterococcus faecalis in complex with N-acetylgalactosamine [Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 10100] |
| 7F7Q_A | 1.46e-69 | 42 | 301 | 32 | 294 | ChainA, GH31 alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase [Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 10100] |
| 7F7R_A | 1.46e-69 | 42 | 301 | 32 | 294 | ChainA, GH31 alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase [Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 10100] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
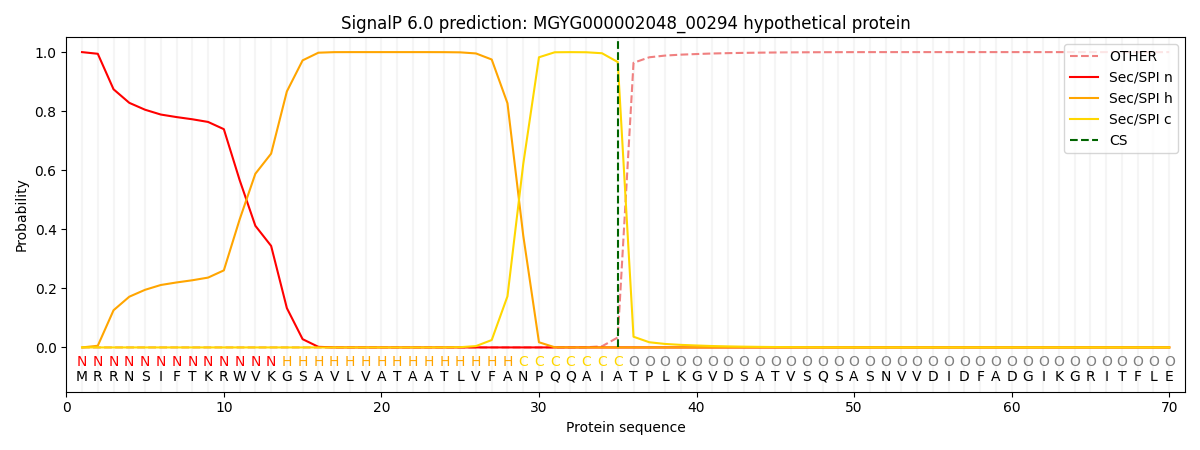
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000460 | 0.998593 | 0.000237 | 0.000257 | 0.000226 | 0.000187 |
