You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002514_03688
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002514_03688
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Proteus mirabilis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Enterobacterales; Enterobacteriaceae; Proteus; Proteus mirabilis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002514_03688 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH23 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 23030; End: 23563 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd13400 | LT_IagB-like | 9.66e-16 | 36 | 173 | 1 | 109 | Escherichia coli invasion protein IagB and similar proteins. Lytic transglycosylase-like protein, similar to Escherichia coli invasion protein IagB. IagB is encoded within a pathogenicity island in Salmonella enterica and has been shown to degrade polymeric peptidoglycan. IagB-like invasion proteins are implicated in the invasion of eukaryotic host cells by bacteria. Lytic transglycosylase (LT) catalyzes the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. Members of this family resemble the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria and the LTs in bacteriophage lambda. |
| pfam01464 | SLT | 1.05e-07 | 29 | 153 | 1 | 94 | Transglycosylase SLT domain. This family is distantly related to pfam00062. Members are found in phages, type II, type III and type IV secretion systems. |
| cd16892 | LT_VirB1-like | 1.18e-06 | 35 | 136 | 6 | 99 | VirB1-like subfamily. This subfamily includes VirB1 protein, one of twelve proteins making up type IV secretion systems (T4SS). T4SS are macromolecular assemblies generally composed of VirB1-11 and VirD4 proteins, and are used by bacteria to transport material across their membranes. VirB1 acts as a lytic transglycosylase (LT), and is important with respect to piercing the peptidoglycan layer in the periplasm. LTs catalyze the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc) as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. Proteins similar to this family include the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria, the LTs in bacteriophage lambda, as well as the eukaryotic "goose-type" lysozymes (goose egg-white lysozyme; GEWL). |
| cd13401 | Slt70-like | 6.93e-06 | 28 | 174 | 9 | 152 | 70kDa soluble lytic transglycosylase (Slt70) and similar proteins. Catalytic domain of the 70kda soluble lytic transglycosylase (LT)-like proteins, which also have an N-terminal U-shaped U-domain and a linker L-domain. LTs catalyze the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. Proteins similar to this family include the soluble and insoluble membrane-bound LTs in bacteria and the LTs in bacteriophage lambda. |
| cd16896 | LT_Slt70-like | 2.91e-05 | 31 | 172 | 10 | 145 | uncharacterized lytic transglycosylase subfamily with similarity to Slt70. Uncharacterized lytic transglycosylase (LT) with a conserved sequence pattern suggesting similarity to the Slt70, a 70kda soluble lytic transglycosylase which also has an N-terminal U-shaped U-domain and a linker L-domain. LTs catalyze the cleavage of the beta-1,4-glycosidic bond between N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc), as do "goose-type" lysozymes. However, in addition to this, they also make a new glycosidic bond with the C6 hydroxyl group of the same muramic acid residue. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QDC33125.1 | 8.07e-123 | 1 | 177 | 1 | 177 |
| ASE71545.1 | 8.07e-123 | 1 | 177 | 1 | 177 |
| QJR98511.1 | 8.07e-123 | 1 | 177 | 1 | 177 |
| SPD98364.1 | 8.07e-123 | 1 | 177 | 1 | 177 |
| AIT32550.1 | 8.07e-123 | 1 | 177 | 1 | 177 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
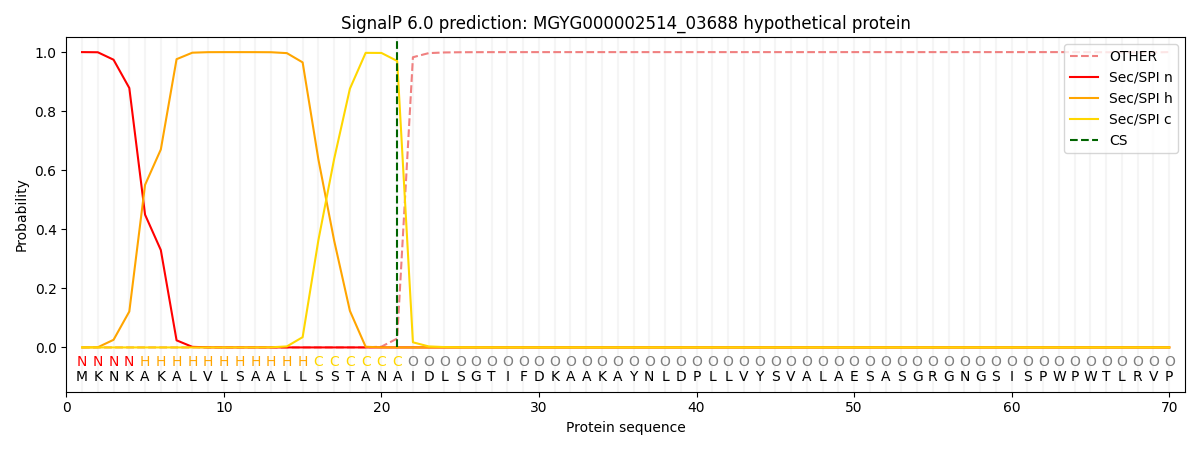
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000668 | 0.998100 | 0.000297 | 0.000325 | 0.000297 | 0.000264 |
