You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002609_02352
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002609_02352
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
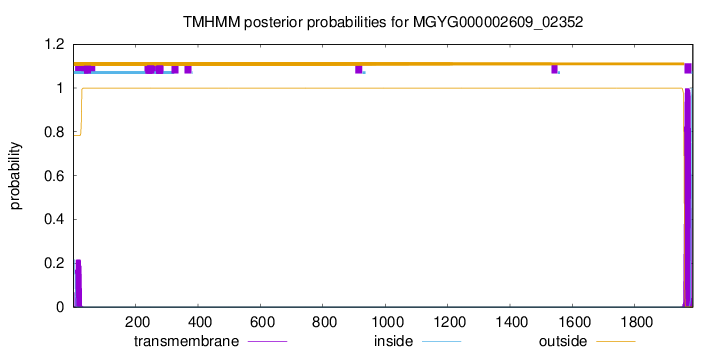
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | CAG-882 sp003486385 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Lachnospirales; Lachnospiraceae; CAG-882; CAG-882 sp003486385 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002609_02352 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH43 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 37283; End: 43243 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH43 | 479 | 796 | 3.3e-137 | 0.9967845659163987 |
| GH10 | 958 | 1328 | 9.3e-84 | 0.9801980198019802 |
| CBM9 | 1484 | 1654 | 2.3e-47 | 0.9835164835164835 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd09003 | GH43_XynD-like | 0.0 | 480 | 798 | 1 | 314 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein such as Bacillus subtilis arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (XynD;BsAXH-m23;BSU18160). This glycosyl hydrolase family 43 (GH43) subgroup includes characterized Bacillus subtilis arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (AXH), Caldicellulosiruptor sp. Tok7B.1 beta-1,4-xylanase (EC 3.2.1.8) / alpha-L-arabinosidase (EC 3.2.1.55) XynA, Caldicellulosiruptor sp. Rt69B.1 xylanase C (EC 3.2.1.8) XynC, and Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37)/ alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55) XynF. It belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. It belongs to the GH43_AXH-like subgroup which includes enzymes that have been annotated as having beta-xylosidase, alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and arabinoxylan alpha-L-1,3-arabinofuranohydrolase, xylanase (endo-alpha-L-arabinanase) as well as AXH activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. AXHs specifically hydrolyze the glycosidic bond between arabinofuranosyl substituents and xylopyranosyl backbone residues of arabinoxylan. Bacillus subtilis AXH (BsAXH-m2,3) has been shown to cleave arabinose units from O-2- or O-3-mono-substituted xylose residues and superposition of its structure with known structures of the GH43 exo-acting enzymes, beta-xylosidase and alpha-L-arabinanase, each in complex with their substrate, reveals a different orientation of the sugar backbone. Several of these enzymes also contain carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs) that bind cellulose or xylan. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| cd08990 | GH43_AXH_like | 1.98e-82 | 489 | 798 | 1 | 269 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 43 protein, includes arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase, beta-xylosidase, endo-1,4-beta-xylanase, and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase. This subgroup includes Bacillus subtilis arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (XynD;BsAXH-m23;BSU18160), Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (Xsa43E;bpr_I2319), Clostridium stercorarium alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase XylA, and metagenomic beta-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.37) / alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase (EC 3.2.1.55) CoXyl43. It belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase clan F (according to carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZY)) which includes family 43 (GH43) and 62 (GH62) families. The GH43_AXH-like subgroup includes enzymes that have been characterized with beta-xylosidase, alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase, endo-alpha-L-arabinanase as well as arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase (AXH) activities. GH43 are inverting enzymes (i.e. they invert the stereochemistry of the anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) that have an aspartate as the catalytic general base, a glutamate as the catalytic general acid and another aspartate that is responsible for pKa modulation and orienting the catalytic acid. Many GH43 enzymes display both alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and beta-D-xylosidase activity using aryl-glycosides as substrates. AXHs specifically hydrolyze the glycosidic bond between arabinofuranosyl substituents and xylopyranosyl backbone residues of arabinoxylan. Metagenomic beta-xylosidase/alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase CoXyl43 shows synergy with Trichoderma reesei cellulases and promotes plant biomass saccharification by degrading xylo-oligosaccharides, such as xylobiose and xylotriose, into the monosaccharide xylose. Studies show that the hydrolytic activity of CoXyl43 is stimulated in the presence of calcium. Several of these enzymes also contain carbohydrate binding modules (CBMs) that bind cellulose or xylan. A common structural feature of GH43 enzymes is a 5-bladed beta-propeller domain that contains the catalytic acid and catalytic base. A long V-shaped groove, partially enclosed at one end, forms a single extended substrate-binding surface across the face of the propeller. |
| pfam00331 | Glyco_hydro_10 | 1.31e-77 | 966 | 1328 | 12 | 310 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 10. |
| smart00633 | Glyco_10 | 5.06e-74 | 1020 | 1326 | 6 | 263 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 10. |
| cd00005 | CBM9_like_1 | 7.00e-68 | 1474 | 1654 | 2 | 184 | DOMON-like type 9 carbohydrate binding module of xylanases. Family 9 carbohydrate-binding modules (CBM9) play a role in the microbial degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose (materials found in plants). The domain has previously been called cellulose-binding domain. The polysaccharide binding sites of CBMs with available 3D structure have been found to be either flat surfaces with interactions formed by predominantly aromatic residues (tryptophan and tyrosine), or extended shallow grooves. The CBM9 domain frequently occurs in tandem repeats; members found in this subfamily typically co-occur with glycosyl hydrolase family 10 domains and are annotated as endo-1,4-beta-xylanases. CBM9 from Thermotoga maritima xylanase 10A is reported to have specificity for polysaccharide reducing ends. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QJU17095.1 | 2.19e-237 | 935 | 1666 | 408 | 1156 |
| ADL32778.1 | 8.61e-223 | 943 | 1656 | 363 | 1063 |
| CBL13458.1 | 2.10e-212 | 944 | 1654 | 350 | 1085 |
| CBK74925.1 | 8.61e-212 | 856 | 1672 | 47 | 885 |
| EEV01588.1 | 1.09e-211 | 944 | 1654 | 350 | 1085 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3C7E_A | 6.02e-119 | 474 | 918 | 8 | 470 | Crystalstructure of a glycoside hydrolase family 43 arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase from Bacillus subtilis. [Bacillus subtilis],3C7F_A Crystal structure of a glycoside hydrolase family 43 arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase from bacillus subtilis in complex with xylotriose. [Bacillus subtilis],3C7H_A Crystal structure of glycoside hydrolase family 43 arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase from Bacillus subtilis in complex with AXOS-4-0.5. [Bacillus subtilis],3C7O_A Crystal structure of a glycoside hydrolase family 43 arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase from Bacillus subtilis in complex with cellotetraose. [Bacillus subtilis] |
| 3C7G_A | 6.21e-119 | 474 | 918 | 9 | 471 | Crystalstructure of a glycoside hydrolase family 43 arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase from Bacillus subtilis in complex with xylotetraose. [Bacillus subtilis] |
| 5A8C_A | 4.27e-68 | 481 | 808 | 30 | 326 | ChainA, CARBOHYDRATE BINDING FAMILY 6 [Acetivibrio thermocellus],5A8D_A Chain A, CARBOHYDRATE BINDING FAMILY 6 [Acetivibrio thermocellus] |
| 4W8L_A | 1.02e-46 | 963 | 1332 | 12 | 347 | Structureof GH10 from Paenibacillus barcinonensis [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],4W8L_B Structure of GH10 from Paenibacillus barcinonensis [Paenibacillus barcinonensis],4W8L_C Structure of GH10 from Paenibacillus barcinonensis [Paenibacillus barcinonensis] |
| 6D5C_A | 1.51e-45 | 962 | 1328 | 29 | 349 | Structureof Caldicellulosiruptor danielii GH10 module of glycoside hydrolase WP_045175321 [Caldicellulosiruptor danielii],6D5C_B Structure of Caldicellulosiruptor danielii GH10 module of glycoside hydrolase WP_045175321 [Caldicellulosiruptor danielii],6D5C_C Structure of Caldicellulosiruptor danielii GH10 module of glycoside hydrolase WP_045175321 [Caldicellulosiruptor danielii] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P45796 | 4.02e-129 | 466 | 925 | 25 | 505 | Arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase OS=Paenibacillus polymyxa OX=1406 GN=xynD PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q45071 | 7.50e-118 | 474 | 918 | 34 | 496 | Arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=xynD PE=1 SV=2 |
| Q60042 | 1.24e-92 | 886 | 1654 | 312 | 1053 | Endo-1,4-beta-xylanase A OS=Thermotoga neapolitana OX=2337 GN=xynA PE=1 SV=1 |
| P38535 | 9.83e-90 | 813 | 1657 | 58 | 897 | Exoglucanase XynX OS=Acetivibrio thermocellus OX=1515 GN=xynX PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q60037 | 2.80e-89 | 886 | 1654 | 316 | 1057 | Endo-1,4-beta-xylanase A OS=Thermotoga maritima (strain ATCC 43589 / DSM 3109 / JCM 10099 / NBRC 100826 / MSB8) OX=243274 GN=xynA PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP

| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000270 | 0.998987 | 0.000202 | 0.000175 | 0.000171 | 0.000157 |