You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002643_01305
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002643_01305
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Turicimonas sp900542195 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Gammaproteobacteria; Burkholderiales; Burkholderiaceae; Turicimonas; Turicimonas sp900542195 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002643_01305 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT2 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit [UDP-forming] | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 22179; End: 24839 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 289 | 460 | 3.4e-37 | 0.9941176470588236 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIGR03030 | CelA | 0.0 | 176 | 846 | 21 | 712 | cellulose synthase catalytic subunit (UDP-forming). Cellulose synthase catalyzes the beta-1,4 polymerization of glucose residues in the formation of cellulose. In bacteria, the substrate is UDP-glucose. The synthase consists of two subunits (or domains in the frequent cases where it is encoded as a single polypeptide), the catalytic domain modelled here and the regulatory domain (pfam03170). The regulatory domain binds the allosteric activator cyclic di-GMP. The protein is membrane-associated and probably assembles into multimers such that the individual cellulose strands can self-assemble into multi-strand fibrils. |
| PRK11498 | bcsA | 0.0 | 24 | 881 | 14 | 851 | cellulose synthase catalytic subunit; Provisional |
| cd06421 | CESA_CelA_like | 3.42e-120 | 286 | 518 | 1 | 234 | CESA_CelA_like are involved in the elongation of the glucan chain of cellulose. Family of proteins related to Agrobacterium tumefaciens CelA and Gluconacetobacter xylinus BscA. These proteins are involved in the elongation of the glucan chain of cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues. They are putative catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase, which is a glycosyltransferase using UDP-glucose as the substrate. The catalytic subunit is an integral membrane protein with 6 transmembrane segments and it is postulated that the protein is anchored in the membrane at the N-terminal end. |
| COG1215 | BcsA | 2.33e-57 | 243 | 698 | 10 | 430 | Glycosyltransferase, catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase and poly-beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine synthase [Cell motility]. |
| cd06437 | CESA_CaSu_A2 | 1.45e-33 | 286 | 513 | 1 | 231 | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit A2 (CESA2) is a catalytic subunit or a catalytic subunit substitute of the cellulose synthase complex. Cellulose synthase (CESA) catalyzes the polymerization reaction of cellulose using UDP-glucose as the substrate. Cellulose is an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues, which is an abundant polysaccharide produced by plants and in varying degrees by several other organisms including algae, bacteria, fungi, and even some animals. Genomes from higher plants harbor multiple CESA genes. There are ten in Arabidopsis. At least three different CESA proteins are required to form a functional complex. In Arabidopsis, CESA1, 3 and 6 and CESA4, 7 and 8, are required for cellulose biosynthesis during primary and secondary cell wall formation. CESA2 is very closely related to CESA6 and is viewed as a prime substitute for CESA6. They functionally compensate each other. The cesa2 and cesa6 double mutant plants were significantly smaller, while the single mutant plants were almost normal. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QQQ96025.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 886 | 1 | 886 |
| ANU67170.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 886 | 1 | 886 |
| QQS88758.1 | 1.38e-294 | 30 | 873 | 29 | 860 |
| QDA53875.1 | 6.11e-287 | 34 | 874 | 33 | 874 |
| QDA53780.1 | 3.30e-270 | 164 | 873 | 61 | 766 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7LBY_A | 3.93e-255 | 22 | 881 | 25 | 863 | ChainA, Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit [UDP-forming] [Escherichia coli K-12] |
| 5EJ1_A | 9.58e-99 | 225 | 836 | 67 | 708 | ChainA, Putative cellulose synthase [Cereibacter sphaeroides 2.4.1] |
| 4HG6_A | 5.18e-98 | 225 | 836 | 79 | 720 | ChainA, Cellulose Synthase Subunit A [Cereibacter sphaeroides] |
| 4P00_A | 5.29e-98 | 225 | 836 | 80 | 721 | ChainA, Cellulose Synthase A subunit [Cereibacter sphaeroides 2.4.1],4P02_A Chain A, Cellulose Synthase subunit A [Cereibacter sphaeroides 2.4.1],5EIY_A Chain A, Putative cellulose synthase [Cereibacter sphaeroides 2.4.1],5EJZ_A Chain A, Putative cellulose synthase [Cereibacter sphaeroides 2.4.1] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P37653 | 1.20e-255 | 22 | 881 | 25 | 863 | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit [UDP-forming] OS=Escherichia coli (strain K12) OX=83333 GN=bcsA PE=1 SV=3 |
| Q8Z291 | 1.28e-255 | 22 | 874 | 25 | 857 | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit [UDP-forming] OS=Salmonella typhi OX=90370 GN=bcsA PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q8X5L7 | 2.39e-255 | 22 | 881 | 25 | 863 | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit [UDP-forming] OS=Escherichia coli O157:H7 OX=83334 GN=bcsA PE=3 SV=2 |
| Q93IN2 | 7.24e-255 | 22 | 874 | 25 | 857 | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit [UDP-forming] OS=Salmonella typhimurium (strain LT2 / SGSC1412 / ATCC 700720) OX=99287 GN=bcsA PE=3 SV=1 |
| P58931 | 3.16e-206 | 154 | 834 | 33 | 699 | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit [UDP-forming] OS=Pseudomonas fluorescens (strain SBW25) OX=216595 GN=bcsA PE=3 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.999974 | 0.000077 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
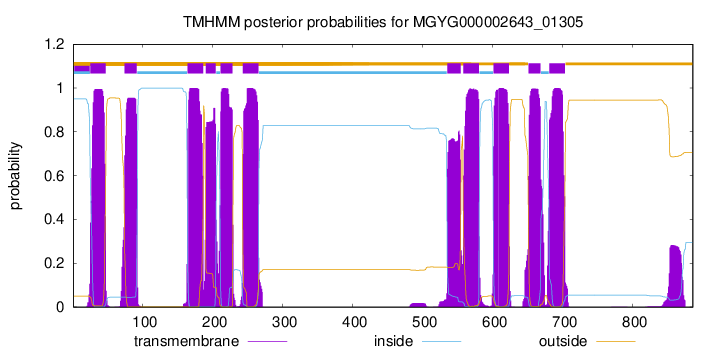
| start | end |
|---|---|
| 25 | 47 |
| 74 | 91 |
| 164 | 186 |
| 190 | 204 |
| 211 | 228 |
| 243 | 265 |
| 535 | 554 |
| 558 | 580 |
| 601 | 623 |
| 651 | 668 |
| 681 | 703 |
