You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000002956_00089
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000002956_00089
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
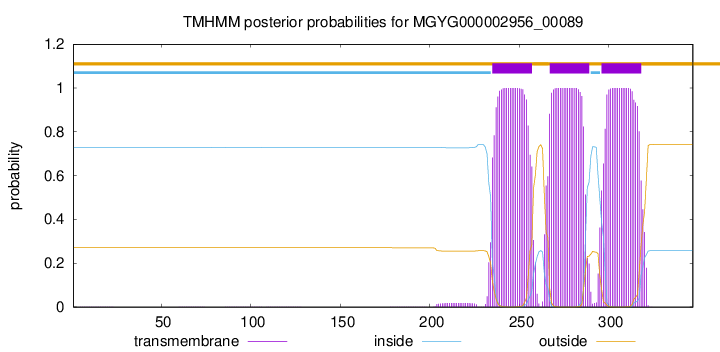
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Lactobacillus kalixensis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Lactobacillales; Lactobacillaceae; Lactobacillus; Lactobacillus kalixensis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000002956_00089 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT2 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | Beta-monoglucosyldiacylglycerol synthase | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 12909; End: 13952 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 71 | 273 | 5.7e-18 | 0.9441624365482234 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd06436 | GlcNAc-1-P_transferase | 6.34e-48 | 5 | 164 | 29 | 191 | N-acetyl-glucosamine transferase is involved in the synthesis of Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. N-acetyl-glucosamine transferase is responsible for the synthesis of bacteria Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (PGA). Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine is a homopolymer that serves as an adhesion for the maintenance of biofilm structural stability in diverse eubacteria. N-acetyl-glucosamine transferase is the product of gene pgaC. Genetic analysis indicated that all four genes of the pgaABCD locus were required for the PGA production, pgaC being a glycosyltransferase. |
| COG1215 | BcsA | 1.15e-22 | 2 | 324 | 85 | 406 | Glycosyltransferase, catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase and poly-beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine synthase [Cell motility]. |
| cd06423 | CESA_like | 1.95e-16 | 5 | 164 | 30 | 180 | CESA_like is the cellulose synthase superfamily. The cellulose synthase (CESA) superfamily includes a wide variety of glycosyltransferase family 2 enzymes that share the common characteristic of catalyzing the elongation of polysaccharide chains. The members include cellulose synthase catalytic subunit, chitin synthase, glucan biosynthesis protein and other families of CESA-like proteins. Cellulose synthase catalyzes the polymerization reaction of cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues in plants, most algae, some bacteria and fungi, and even some animals. In bacteria, algae and lower eukaryotes, there is a second unrelated type of cellulose synthase (Type II), which produces acylated cellulose, a derivative of cellulose. Chitin synthase catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin, which is a linear homopolymer of beta-(1,4)-linked GlcNAc residues and Glucan Biosynthesis protein catalyzes the elongation of beta-1,2 polyglucose chains of Glucan. |
| pfam13632 | Glyco_trans_2_3 | 9.99e-15 | 71 | 256 | 4 | 194 | Glycosyl transferase family group 2. Members of this family of prokaryotic proteins include putative glucosyltransferases, which are involved in bacterial capsule biosynthesis. |
| cd06437 | CESA_CaSu_A2 | 4.20e-11 | 6 | 208 | 37 | 232 | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit A2 (CESA2) is a catalytic subunit or a catalytic subunit substitute of the cellulose synthase complex. Cellulose synthase (CESA) catalyzes the polymerization reaction of cellulose using UDP-glucose as the substrate. Cellulose is an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues, which is an abundant polysaccharide produced by plants and in varying degrees by several other organisms including algae, bacteria, fungi, and even some animals. Genomes from higher plants harbor multiple CESA genes. There are ten in Arabidopsis. At least three different CESA proteins are required to form a functional complex. In Arabidopsis, CESA1, 3 and 6 and CESA4, 7 and 8, are required for cellulose biosynthesis during primary and secondary cell wall formation. CESA2 is very closely related to CESA6 and is viewed as a prime substitute for CESA6. They functionally compensate each other. The cesa2 and cesa6 double mutant plants were significantly smaller, while the single mutant plants were almost normal. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AJT50840.1 | 4.10e-146 | 2 | 336 | 63 | 396 |
| APG69196.1 | 4.54e-138 | 2 | 336 | 54 | 386 |
| ASW63993.1 | 4.54e-138 | 2 | 336 | 54 | 386 |
| BCQ32634.1 | 1.30e-137 | 2 | 336 | 54 | 386 |
| AGQ23556.1 | 6.03e-136 | 2 | 336 | 54 | 386 |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P74165 | 2.16e-14 | 6 | 216 | 144 | 344 | Beta-monoglucosyldiacylglycerol synthase OS=Synechocystis sp. (strain PCC 6803 / Kazusa) OX=1111708 GN=sll1377 PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q5HKQ0 | 3.76e-09 | 4 | 267 | 79 | 326 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase OS=Staphylococcus epidermidis (strain ATCC 35984 / RP62A) OX=176279 GN=icaA PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q8GLC5 | 5.02e-08 | 4 | 267 | 79 | 326 | Poly-beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine synthase OS=Staphylococcus epidermidis OX=1282 GN=icaA PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q7PC67 | 8.18e-07 | 52 | 256 | 221 | 423 | Probable glucomannan 4-beta-mannosyltransferase 2 OS=Oryza sativa subsp. japonica OX=39947 GN=CSLA2 PE=2 SV=2 |
| Q9SRT3 | 1.16e-06 | 71 | 235 | 317 | 483 | Probable xyloglucan glycosyltransferase 6 OS=Arabidopsis thaliana OX=3702 GN=CSLC6 PE=1 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
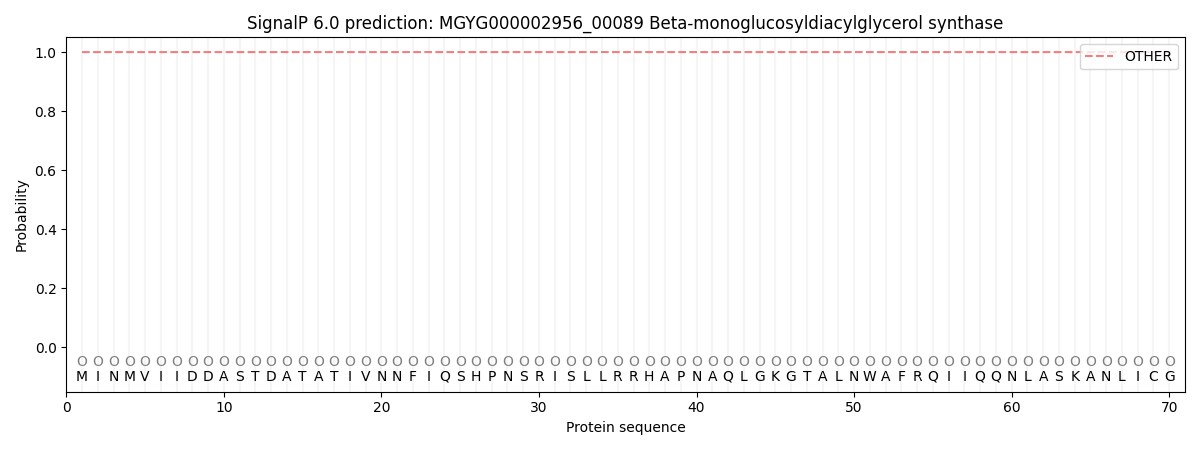
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000059 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |