You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003137_02055
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003137_02055
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Bradyrhizobium sp000015165 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Alphaproteobacteria; Rhizobiales; Xanthobacteraceae; Bradyrhizobium; Bradyrhizobium sp000015165 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003137_02055 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GT2 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 47986; End: 49962 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GT2 | 120 | 292 | 7.1e-26 | 0.9882352941176471 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd06421 | CESA_CelA_like | 5.43e-103 | 117 | 351 | 1 | 234 | CESA_CelA_like are involved in the elongation of the glucan chain of cellulose. Family of proteins related to Agrobacterium tumefaciens CelA and Gluconacetobacter xylinus BscA. These proteins are involved in the elongation of the glucan chain of cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues. They are putative catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase, which is a glycosyltransferase using UDP-glucose as the substrate. The catalytic subunit is an integral membrane protein with 6 transmembrane segments and it is postulated that the protein is anchored in the membrane at the N-terminal end. |
| PRK11498 | bcsA | 7.57e-57 | 117 | 403 | 260 | 548 | cellulose synthase catalytic subunit; Provisional |
| COG1215 | BcsA | 6.86e-56 | 69 | 466 | 10 | 400 | Glycosyltransferase, catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase and poly-beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosamine synthase [Cell motility]. |
| cd06435 | CESA_NdvC_like | 5.50e-34 | 126 | 350 | 7 | 231 | NdvC_like proteins in this family are putative bacterial beta-(1,6)-glucosyltransferase. NdvC_like proteins in this family are putative bacterial beta-(1,6)-glucosyltransferase. Bradyrhizobium japonicum synthesizes periplasmic cyclic beta-(1,3),beta-(1,6)-D-glucans during growth under hypoosmotic conditions. Two genes (ndvB, ndvC) are involved in the beta-(1, 3), beta-(1,6)-glucan synthesis. The ndvC mutant strain resulted in synthesis of altered cyclic beta-glucans composed almost entirely of beta-(1, 3)-glycosyl linkages. The periplasmic cyclic beta-(1,3),beta-(1,6)-D-glucans function for osmoregulation. The ndvC mutation also affects the ability of the bacteria to establish a successful symbiotic interaction with host plant. Thus, the beta-glucans may function as suppressors of a host defense response. |
| cd06423 | CESA_like | 4.39e-27 | 121 | 303 | 1 | 180 | CESA_like is the cellulose synthase superfamily. The cellulose synthase (CESA) superfamily includes a wide variety of glycosyltransferase family 2 enzymes that share the common characteristic of catalyzing the elongation of polysaccharide chains. The members include cellulose synthase catalytic subunit, chitin synthase, glucan biosynthesis protein and other families of CESA-like proteins. Cellulose synthase catalyzes the polymerization reaction of cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues in plants, most algae, some bacteria and fungi, and even some animals. In bacteria, algae and lower eukaryotes, there is a second unrelated type of cellulose synthase (Type II), which produces acylated cellulose, a derivative of cellulose. Chitin synthase catalyzes the incorporation of GlcNAc from substrate UDP-GlcNAc into chitin, which is a linear homopolymer of beta-(1,4)-linked GlcNAc residues and Glucan Biosynthesis protein catalyzes the elongation of beta-1,2 polyglucose chains of Glucan. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABQ35694.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 658 | 1 | 658 |
| SMX57945.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 658 | 1 | 657 |
| BAM90446.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 658 | 1 | 656 |
| SHL43919.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 658 | 20 | 675 |
| SHG58830.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 657 | 1 | 656 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5EJ1_A | 1.98e-56 | 8 | 490 | 22 | 525 | ChainA, Putative cellulose synthase [Cereibacter sphaeroides 2.4.1] |
| 4HG6_A | 4.65e-56 | 8 | 490 | 34 | 537 | ChainA, Cellulose Synthase Subunit A [Cereibacter sphaeroides] |
| 4P00_A | 4.70e-56 | 8 | 490 | 35 | 538 | ChainA, Cellulose Synthase A subunit [Cereibacter sphaeroides 2.4.1],4P02_A Chain A, Cellulose Synthase subunit A [Cereibacter sphaeroides 2.4.1],5EIY_A Chain A, Putative cellulose synthase [Cereibacter sphaeroides 2.4.1],5EJZ_A Chain A, Putative cellulose synthase [Cereibacter sphaeroides 2.4.1] |
| 7LBY_A | 3.32e-55 | 117 | 488 | 273 | 650 | ChainA, Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit [UDP-forming] [Escherichia coli K-12] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q76KJ8 | 1.73e-60 | 31 | 471 | 70 | 500 | Cellulose synthase 1 OS=Komagataeibacter hansenii OX=436 GN=acsAB PE=1 SV=1 |
| P0CW87 | 1.73e-60 | 31 | 471 | 70 | 500 | Cellulose synthase 1 OS=Komagataeibacter xylinus OX=28448 GN=acsAB PE=1 SV=1 |
| P58931 | 2.57e-60 | 115 | 483 | 157 | 522 | Cellulose synthase catalytic subunit [UDP-forming] OS=Pseudomonas fluorescens (strain SBW25) OX=216595 GN=bcsA PE=3 SV=2 |
| Q9RBJ2 | 1.02e-59 | 117 | 475 | 146 | 501 | Putative cellulose synthase 2 OS=Komagataeibacter xylinus OX=28448 GN=bcsABII-A PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q9WX75 | 1.02e-59 | 117 | 475 | 146 | 501 | Putative cellulose synthase 3 OS=Komagataeibacter xylinus OX=28448 GN=bcsABII-B PE=3 SV=1 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as OTHER
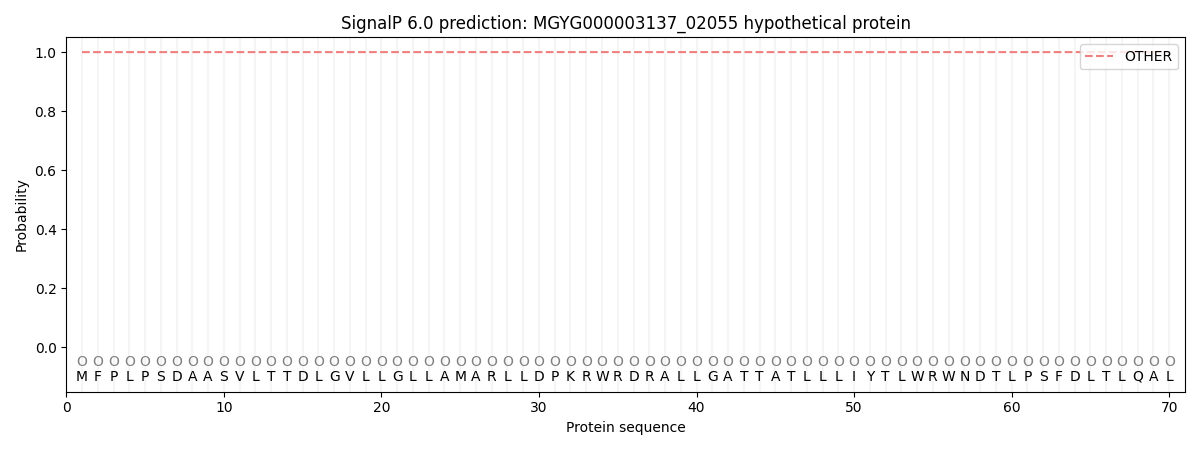
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.000006 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
TMHMM Annotations download full data without filtering help
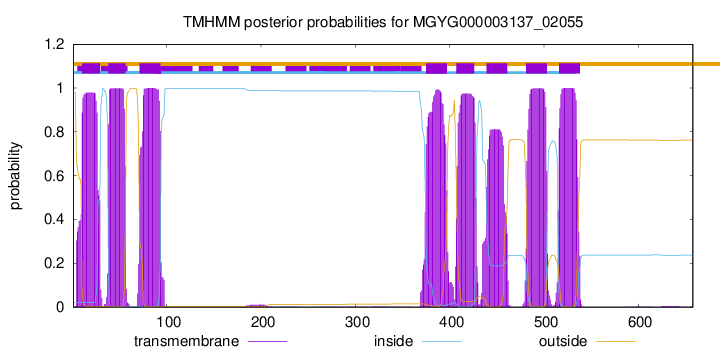
| start | end |
|---|---|
| 10 | 29 |
| 38 | 56 |
| 71 | 93 |
| 375 | 397 |
| 407 | 426 |
| 439 | 461 |
| 481 | 503 |
| 516 | 538 |
