You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003237_03665
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003237_03665
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Victivallis sp002998355 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Verrucomicrobiota; Lentisphaeria; Victivallales; Victivallaceae; Victivallis; Victivallis sp002998355 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003237_03665 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH39 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 27658; End: 30969 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH39 | 356 | 657 | 4.4e-30 | 0.7424593967517401 |
| CBM9 | 937 | 1102 | 2.9e-21 | 0.8681318681318682 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd09621 | CBM9_like_5 | 3.59e-47 | 918 | 1102 | 1 | 188 | DOMON-like type 9 carbohydrate binding module. Family 9 carbohydrate-binding modules (CBM9) play a role in the microbial degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose (materials found in plants). The domain has previously been called cellulose-binding domain. The polysaccharide binding sites of CBMs with available 3D structure have been found to be either flat surfaces with interactions formed by predominantly aromatic residues (tryptophan and tyrosine), or extended shallow grooves. CBM9 domains found in this uncharacterized heterogeneous subfamily are often located at the C-terminus of longer proteins and may co-occur with various other functional domains such as glycosyl hydrolases. The CBM9 module in these architectures may be involved in binding to carbohydrates. |
| cd09619 | CBM9_like_4 | 2.24e-15 | 918 | 1075 | 14 | 162 | DOMON-like type 9 carbohydrate binding module. Family 9 carbohydrate-binding modules (CBM9) play a role in the microbial degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose (materials found in plants). The domain has previously been called cellulose-binding domain. The polysaccharide binding sites of CBMs with available 3D structure have been found to be either flat surfaces with interactions formed by predominantly aromatic residues (tryptophan and tyrosine), or extended shallow grooves. CBM9 domains found in this uncharacterized heterogeneous subfamily are often located at the C-terminus of longer proteins and may co-occur with various other domains. |
| pfam06452 | CBM9_1 | 2.07e-13 | 942 | 1102 | 30 | 181 | Carbohydrate family 9 binding domain-like. CBM9_1 is a C-terminal domain on bacterial xylanase proteins, and it is tandemly repeated in a number of family-members. The CBM9 module binds to amorphous and crystalline cellulose and a range of soluble di- and monosaccharides as well as to cello- and xylo- oligomers of different degrees of polymerization. Comparison of the glucose and cellobiose complexes during crystallisation reveals surprising differences in binding of these two substrates by CBM9-2. Cellobiose was found to bind in a distinct orientation from glucose, while still maintaining optimal stacking and electrostatic interactions with the reducing end sugar. |
| cd08995 | GH32_EcAec43-like | 2.49e-11 | 49 | 195 | 8 | 168 | Glycosyl hydrolase family 32, such as the putative glycoside hydrolase Escherichia coli Aec43 (FosGH2). This glycosyl hydrolase family 32 (GH32) subgroup includes Escherichia coli strain BEN2908 putative glycoside hydrolase Aec43 (FosGH2). GH32 enzymes cleave sucrose into fructose and glucose via beta-fructofuranosidase activity, producing invert sugar that is a mixture of dextrorotatory D-glucose and levorotatory D-fructose, thus named invertase (EC 3.2.1.26). GH32 family also contains other fructofuranosidases such as inulinase (EC 3.2.1.7), exo-inulinase (EC 3.2.1.80), levanase (EC 3.2.1.65), and transfructosidases such sucrose:sucrose 1-fructosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.99), fructan:fructan 1-fructosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.100), sucrose:fructan 6-fructosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.10), fructan:fructan 6G-fructosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.243) and levan fructosyltransferases (EC 2.4.1.-). These retaining enzymes (i.e. they retain the configuration at anomeric carbon atom of the substrate) catalyze hydrolysis in two steps involving a covalent glycosyl enzyme intermediate: an aspartate located close to the N-terminus acts as the catalytic nucleophile and a glutamate acts as the general acid/base; a conserved aspartate residue in the Arg-Asp-Pro (RDP) motif stabilizes the transition state. These enzymes are predicted to display a 5-fold beta-propeller fold as found for GH43 and CH68. The breakdown of sucrose is widely used as a carbon or energy source by bacteria, fungi, and plants. Invertase is used commercially in the confectionery industry, since fructose has a sweeter taste than sucrose and a lower tendency to crystallize. |
| cd00241 | DOMON_like | 2.53e-11 | 930 | 1084 | 5 | 158 | Domon-like ligand-binding domains. DOMON-like domains can be found in all three kindgoms of life and are a diverse group of ligand binding domains that have been shown to interact with sugars and hemes. DOMON domains were initially thought to confer protein-protein interactions. They were subsequently found as a heme-binding motif in cellobiose dehydrogenase, an extracellular fungal oxidoreductase that degrades both lignin and cellulose, and in ethylbenzene dehydrogenase, an enzyme that aids in the anaerobic degradation of hydrocarbons. The domain interacts with sugars in the type 9 carbohydrate binding modules (CBM9), which are present in a variety of glycosyl hydrolases, and it can also be found at the N-terminus of sensor histidine kinases. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVM44950.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 1103 | 1 | 1103 |
| QTH43804.1 | 8.78e-43 | 319 | 1100 | 320 | 1111 |
| ACZ43011.1 | 2.13e-42 | 413 | 1099 | 402 | 1271 |
| ACZ43418.1 | 1.62e-41 | 334 | 1099 | 351 | 1030 |
| AHF89595.1 | 6.92e-41 | 334 | 1094 | 169 | 861 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5MRJ_A | 3.68e-06 | 344 | 467 | 139 | 259 | Crystalstructure of Endo-1,4-beta-xylanase-like protein from Acremonium chrysogenum [Acremonium chrysogenum ATCC 11550],5MRJ_B Crystal structure of Endo-1,4-beta-xylanase-like protein from Acremonium chrysogenum [Acremonium chrysogenum ATCC 11550] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
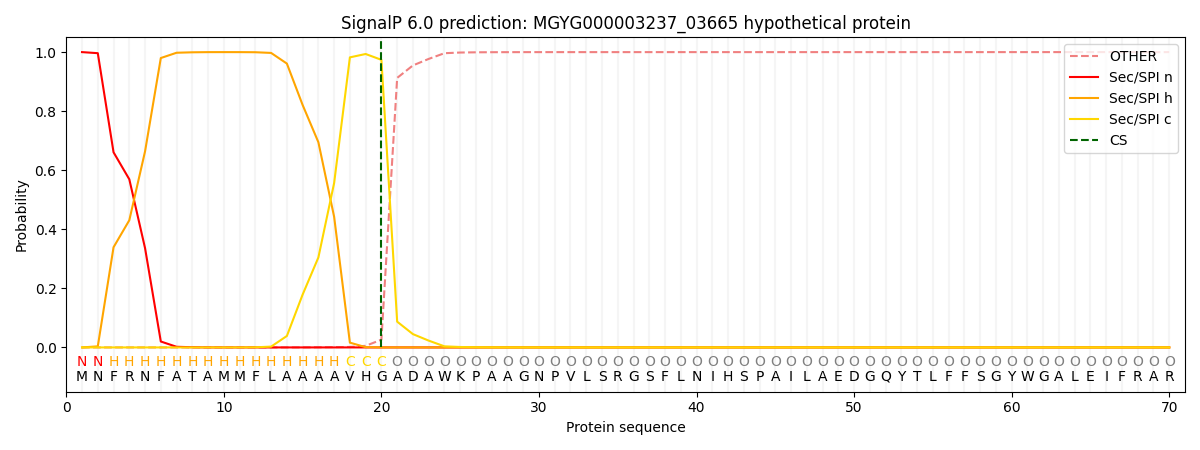
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000472 | 0.998670 | 0.000234 | 0.000211 | 0.000197 | 0.000187 |
