You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000003514_02374
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000003514_02374
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Fibrobacter_A intestinalis | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Fibrobacterota; Fibrobacteria; Fibrobacterales; Fibrobacteraceae; Fibrobacter_A; Fibrobacter_A intestinalis | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000003514_02374 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CE12 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 500; End: 2239 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CE12 | 26 | 243 | 1.6e-53 | 0.9952380952380953 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd01821 | Rhamnogalacturan_acetylesterase_like | 1.94e-48 | 26 | 243 | 2 | 198 | Rhamnogalacturan_acetylesterase_like subgroup of SGNH-hydrolases. Rhamnogalacturan acetylesterase removes acetyl esters from rhamnogalacturonan substrates, and renders them susceptible to degradation by rhamnogalacturonases. Rhamnogalacturonans are highly branched regions in pectic polysaccharides, consisting of repeating -(1,2)-L-Rha-(1,4)-D-GalUA disaccharide units, with many rhamnose residues substituted by neutral oligosaccharides such as arabinans, galactans and arabinogalactans. Extracellular enzymes participating in the degradation of plant cell wall polymers, such as Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase, would typically be found in saprophytic and plant pathogenic fungi and bacteria. |
| cd04082 | CBM35_pectate_lyase-like | 2.89e-28 | 408 | 516 | 12 | 120 | Carbohydrate Binding Module family 35 (CBM35), pectate lyase-like; appended mainly to enzymes that bind mannan (Man), xylan, glucuronic acid (GlcA) and possibly glucans. This family includes carbohydrate binding module family 35 (CBM35) domains that are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains that are appended mainly to enzymes that bind mannan (Man), xylan, glucuronic acid (GlcA) and possibly glucans. Included in this family are CBM35s of pectate lyases, including pectate lyase 10A from Cellvibrio japonicas, these enzymes release delta-4,5-anhydrogalaturonic acid (delta4,5-GalA) from pectin, thus identifying a signature molecule for plant cell wall degradation. CBM35s are unique in that they display conserved specificity through extensive sequence similarity but divergent function through their appended catalytic modules. They are known to bind alpha-D-galactose (Gal), mannan (Man), xylan, glucuronic acid (GlcA), a beta-polymer of mannose, and possibly glucans, forming four subfamilies based on general ligand specificities (galacto, urono, manno, and gluco configurations). In contrast to most CBMs that are generally rigid proteins, CBM35 undergoes significant conformational change upon ligand binding. Some CBM35s bind their ligands in a calcium-dependent manner, especially those binding uronic acids. |
| COG2755 | TesA | 9.50e-21 | 18 | 247 | 2 | 208 | Lysophospholipase L1 or related esterase [Amino acid transport and metabolism]. |
| cd04083 | CBM35_Lmo2446-like | 5.52e-12 | 406 | 490 | 11 | 95 | Carbohydrate Binding Module 35 (CBM35) domains similar to Lmo2446. This family includes carbohydrate binding module 35 (CBM35) domains that are appended to several carbohydrate binding enzymes. Some CBM35 domains belonging to this family are appended to glycoside hydrolase (GH) family domains, including glycoside hydrolase family 31 (GH31), for example the CBM35 domain of Lmo2446, an uncharacterized protein from Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e. These CBM35s are non-catalytic carbohydrate binding domains that facilitate the strong binding of the GH catalytic modules with their dedicated, insoluble substrates. GH31 has a wide range of hydrolytic activities such as alpha-glucosidase, alpha-xylosidase, 6-alpha-glucosyltransferase, or alpha-1,4-glucan lyase, cleaving a terminal carbohydrate moiety from a substrate that may be a starch or a glycoprotein. Most characterized GH31 enzymes are alpha-glucosidases. |
| pfam13472 | Lipase_GDSL_2 | 8.85e-09 | 29 | 183 | 1 | 148 | GDSL-like Lipase/Acylhydrolase family. This family of presumed lipases and related enzymes are similar to pfam00657. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACX76065.1 | 2.29e-168 | 13 | 534 | 13 | 530 |
| ADL25046.1 | 2.61e-168 | 13 | 534 | 17 | 534 |
| ATC63124.1 | 2.93e-42 | 16 | 314 | 84 | 367 |
| AGJ59222.1 | 2.04e-41 | 20 | 239 | 43 | 255 |
| QQM43093.1 | 2.09e-41 | 24 | 239 | 42 | 250 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2W87_A | 7.68e-14 | 408 | 529 | 15 | 136 | Xyl-CBM35in complex with glucuronic acid containing disaccharide. [Cellvibrio japonicus],2W87_B Xyl-CBM35 in complex with glucuronic acid containing disaccharide. [Cellvibrio japonicus] |
| 2W46_A | 8.68e-14 | 408 | 529 | 20 | 141 | CBM35from Cellvibrio japonicus Abf62 [Cellvibrio japonicus],2W46_B CBM35 from Cellvibrio japonicus Abf62 [Cellvibrio japonicus] |
| 2O14_A | 3.13e-13 | 17 | 253 | 155 | 369 | X-RayCrystal Structure of Protein YXIM_BACsu from Bacillus subtilis. Northeast Structural Genomics Consortium Target SR595 [Bacillus subtilis] |
| 2VZP_A | 4.99e-13 | 409 | 518 | 16 | 125 | AtomicResolution Structure of the C-terminal CBM35 from Amycolatopsis orientalis exo-chitosanase CsxA [Amycolatopsis orientalis],2VZP_B Atomic Resolution Structure of the C-terminal CBM35 from Amycolatopsis orientalis exo-chitosanase CsxA [Amycolatopsis orientalis],2VZQ_A C-terminal CBM35 from Amycolatopsis orientalis exo-chitosanase CsxA in complex with digalacturonic acid [Amycolatopsis orientalis],2VZQ_B C-terminal CBM35 from Amycolatopsis orientalis exo-chitosanase CsxA in complex with digalacturonic acid [Amycolatopsis orientalis],2VZR_A C-terminal CBM35 from Amycolatopsis orientalis exo-chitosanase CsxA in complex with glucuronic acid [Amycolatopsis orientalis],2VZR_B C-terminal CBM35 from Amycolatopsis orientalis exo-chitosanase CsxA in complex with glucuronic acid [Amycolatopsis orientalis] |
| 2W3J_A | 2.66e-12 | 394 | 530 | 1 | 136 | Structureof a family 35 carbohydrate binding module from an environmental isolate [uncultured bacterium] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O31523 | 2.00e-31 | 27 | 245 | 8 | 214 | Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase RhgT OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=rhgT PE=1 SV=1 |
| O31528 | 3.30e-27 | 27 | 237 | 5 | 204 | Probable rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase YesY OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=yesY PE=1 SV=1 |
| P42304 | 7.56e-13 | 17 | 245 | 170 | 376 | Uncharacterized esterase YxiM OS=Bacillus subtilis (strain 168) OX=224308 GN=yxiM PE=1 SV=2 |
| P23030 | 2.50e-11 | 408 | 529 | 175 | 296 | Endo-1,4-beta-xylanase B OS=Cellvibrio japonicus (strain Ueda107) OX=498211 GN=xynB PE=1 SV=2 |
| P23031 | 2.57e-11 | 408 | 529 | 175 | 296 | Alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase C OS=Cellvibrio japonicus (strain Ueda107) OX=498211 GN=xynC PE=1 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
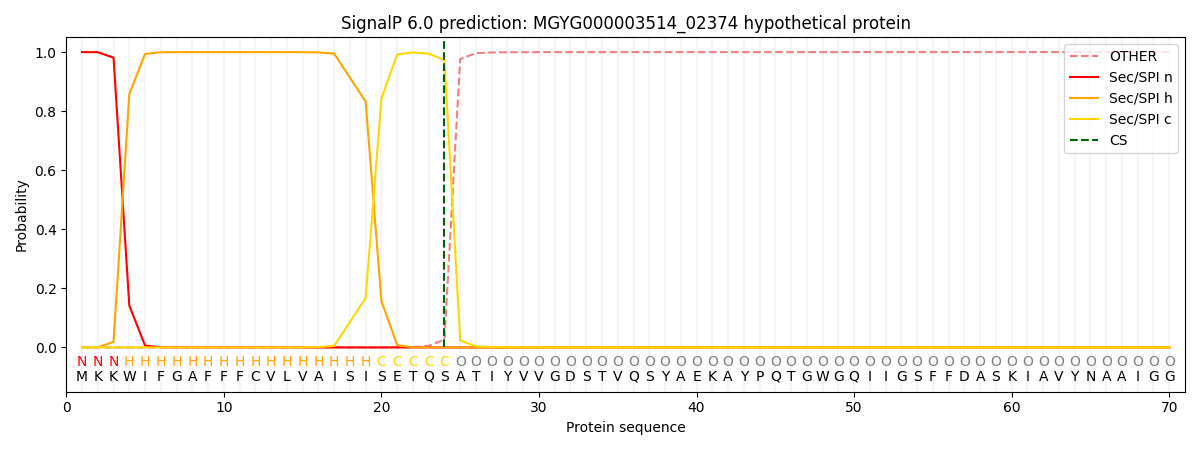
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000238 | 0.999147 | 0.000174 | 0.000152 | 0.000138 | 0.000138 |
