You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004244_00403
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004244_00403
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
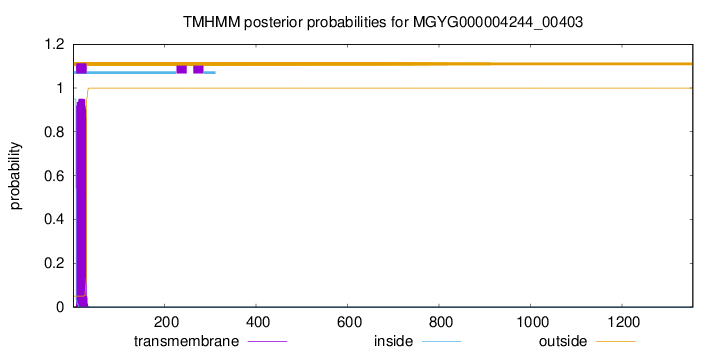
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | UMGS1601 sp900553335 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Oscillospirales; Ruminococcaceae; UMGS1601; UMGS1601 sp900553335 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004244_00403 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH5 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 134695; End: 138762 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH5 | 496 | 768 | 3.1e-73 | 0.9927536231884058 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam00150 | Cellulase | 1.41e-49 | 496 | 766 | 15 | 267 | Cellulase (glycosyl hydrolase family 5). |
| COG2730 | BglC | 4.18e-17 | 474 | 735 | 48 | 331 | Aryl-phospho-beta-D-glucosidase BglC, GH1 family [Carbohydrate transport and metabolism]. |
| cd14256 | Dockerin_I | 1.91e-12 | 1293 | 1347 | 1 | 55 | Type I dockerin repeat domain. Bacterial cohesin domains bind to a complementary protein domain named dockerin, and this interaction is required for the formation of the cellulosome, a cellulose-degrading complex. The cellulosome consists of scaffoldin, a noncatalytic scaffolding polypeptide, that comprises repeating cohesion modules and a single carbohydrate-binding module (CBM). Specific calcium-dependent interactions between cohesins and dockerins appear to be essential for cellulosome assembly. This subfamily represents type I dockerins, which are responsible for anchoring a variety of enzymatic domains to the complex. |
| pfam00404 | Dockerin_1 | 4.33e-06 | 1294 | 1345 | 1 | 52 | Dockerin type I repeat. The dockerin repeat is the binding partner of the cohesin domain pfam00963. The cohesin-dockerin interaction is the crucial interaction for complex formation in the cellulosome. The dockerin repeats, each bearing homology to the EF-hand calcium-binding loop bind calcium. |
| cd14254 | Dockerin_II | 2.84e-05 | 1294 | 1347 | 1 | 52 | Type II dockerin repeat domain. Bacterial cohesin domains bind to a complementary protein domain named dockerin, and this interaction is required for the formation of the cellulosome, a cellulose-degrading complex. The cellulosome consists of scaffoldin, a noncatalytic scaffolding polypeptide, that comprises repeating cohesion modules and a single carbohydrate-binding module (CBM). Specific calcium-dependent interactions between cohesins and dockerins appear to be essential for cellulosome assembly. This subfamily represents type II dockerins, which are responsible for mediating attachment of the cellulosome complex to the bacterial cell wall. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUO18792.1 | 4.72e-276 | 5 | 1260 | 4 | 1044 |
| AUO19859.1 | 1.33e-153 | 392 | 994 | 37 | 645 |
| BCN29385.1 | 8.28e-64 | 465 | 1155 | 349 | 950 |
| AIQ47948.1 | 3.41e-60 | 465 | 799 | 36 | 400 |
| AIQ53446.1 | 1.34e-58 | 465 | 799 | 36 | 400 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2JEP_A | 5.47e-56 | 469 | 799 | 34 | 394 | Nativefamily 5 xyloglucanase from Paenibacillus pabuli [Paenibacillus pabuli],2JEP_B Native family 5 xyloglucanase from Paenibacillus pabuli [Paenibacillus pabuli],2JEQ_A Family 5 xyloglucanase from Paenibacillus pabuli in complex with ligand [Paenibacillus pabuli] |
| 6WQP_A | 9.55e-51 | 466 | 774 | 12 | 331 | GH5-4broad specificity endoglucanase from Ruminococcus champanellensis [Ruminococcus champanellensis],6WQP_B GH5-4 broad specificity endoglucanase from Ruminococcus champanellensis [Ruminococcus champanellensis],6WQV_A GH5-4 broad specificity endoglucanase from Ruminococcus champanellensis with bound cellotriose [Ruminococcus champanellensis],6WQV_B GH5-4 broad specificity endoglucanase from Ruminococcus champanellensis with bound cellotriose [Ruminococcus champanellensis],6WQV_C GH5-4 broad specificity endoglucanase from Ruminococcus champanellensis with bound cellotriose [Ruminococcus champanellensis],6WQV_D GH5-4 broad specificity endoglucanase from Ruminococcus champanellensis with bound cellotriose [Ruminococcus champanellensis] |
| 6Q1I_A | 1.03e-50 | 469 | 802 | 13 | 352 | GH5-4broad specificity endoglucanase from Clostrdium longisporum [Clostridium longisporum],6Q1I_B GH5-4 broad specificity endoglucanase from Clostrdium longisporum [Clostridium longisporum] |
| 6PZ7_A | 9.05e-50 | 467 | 797 | 6 | 335 | GH5-4broad specificity endoglucanase from Clostridium acetobutylicum [Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824] |
| 4IM4_A | 2.33e-49 | 466 | 802 | 3 | 334 | ChainA, Endoglucanase E [Acetivibrio thermocellus],4IM4_B Chain B, Endoglucanase E [Acetivibrio thermocellus],4IM4_C Chain C, Endoglucanase E [Acetivibrio thermocellus],4IM4_D Chain D, Endoglucanase E [Acetivibrio thermocellus],4IM4_E Chain E, Endoglucanase E [Acetivibrio thermocellus],4IM4_F Chain F, Endoglucanase E [Acetivibrio thermocellus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O08342 | 2.18e-56 | 460 | 799 | 30 | 399 | Endoglucanase A OS=Paenibacillus barcinonensis OX=198119 GN=celA PE=1 SV=1 |
| P54937 | 3.67e-49 | 469 | 802 | 38 | 377 | Endoglucanase A OS=Clostridium longisporum OX=1523 GN=celA PE=1 SV=1 |
| P23660 | 1.40e-46 | 466 | 799 | 23 | 359 | Endoglucanase A OS=Ruminococcus albus OX=1264 GN=celA PE=1 SV=1 |
| P28621 | 4.58e-46 | 458 | 806 | 24 | 377 | Endoglucanase B OS=Clostridium cellulovorans (strain ATCC 35296 / DSM 3052 / OCM 3 / 743B) OX=573061 GN=engB PE=3 SV=1 |
| P10477 | 9.84e-46 | 466 | 807 | 53 | 389 | Cellulase/esterase CelE OS=Acetivibrio thermocellus (strain ATCC 27405 / DSM 1237 / JCM 9322 / NBRC 103400 / NCIMB 10682 / NRRL B-4536 / VPI 7372) OX=203119 GN=celE PE=1 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as LIPO
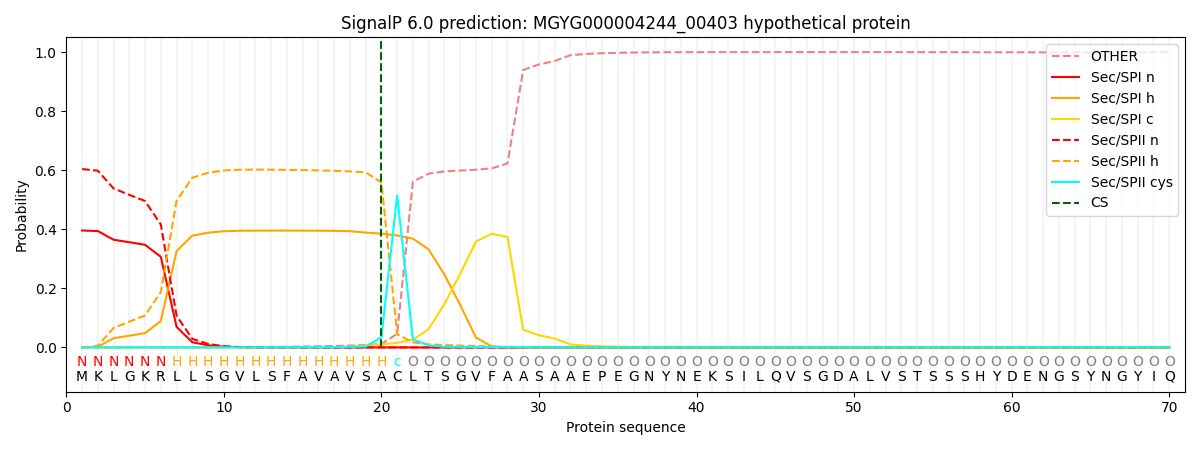
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000449 | 0.390134 | 0.608772 | 0.000325 | 0.000169 | 0.000126 |