You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004290_01093
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004290_01093
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | Alistipes sp900549305 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Rikenellaceae; Alistipes; Alistipes sp900549305 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004290_01093 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | PL10 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 1414; End: 3000 Strand: + | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL10 | 111 | 392 | 1.3e-111 | 0.9927272727272727 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIGR02474 | pec_lyase | 5.94e-25 | 111 | 307 | 1 | 196 | pectate lyase, PelA/Pel-15E family. Members of this family are isozymes of pectate lyase (EC 4.2.2.2), also called polygalacturonic transeliminase and alpha-1,4-D-endopolygalacturonic acid lyase. [Energy metabolism, Biosynthesis and degradation of polysaccharides] |
| pfam09492 | Pec_lyase | 3.20e-20 | 111 | 307 | 1 | 194 | Pectic acid lyase. Members of this family are isozymes of pectate lyase (EC:4.2.2.2), also called polygalacturonic transeliminase and alpha-1,4-D-endopolygalacturonic acid lyase. |
| pfam09492 | Pec_lyase | 5.72e-08 | 47 | 204 | 5 | 158 | Pectic acid lyase. Members of this family are isozymes of pectate lyase (EC:4.2.2.2), also called polygalacturonic transeliminase and alpha-1,4-D-endopolygalacturonic acid lyase. |
| cd02889 | SQCY | 0.004 | 158 | 204 | 166 | 214 | Squalene cyclase (SQCY) domain; found in class II terpene cyclases that have an alpha 6 - alpha 6 barrel fold. Squalene cyclase (SQCY) and 2,3-oxidosqualene cyclase (OSQCY) are integral membrane proteins that catalyze a cationic cyclization cascade converting linear triterpenes to fused ring compounds. Bacterial SQCY catalyzes the convertion of squalene to hopene or diplopterol. Eukaryotic OSQCY transforms the 2,3-epoxide of squalene to compounds such as, lanosterol (a metabolic precursor of cholesterol and steroid hormones) in mammals and fungi or, cycloartenol in plants. Deletion of a single glycine residue of Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius SQCY alters its substrate specificity into that of eukaryotic OSQCY. Both enzymes have a second minor domain, which forms an alpha-alpha barrel that is inserted into the major domain. This group also contains SQCY-like archael sequences and some bacterial SQCY's which lack this minor domain. |
| TIGR01787 | squalene_cyclas | 0.004 | 30 | 118 | 509 | 587 | squalene/oxidosqualene cyclases. This family of enzymes catalyzes the cyclization of the triterpenes squalene or 2-3-oxidosqualene to a variety of products including hopene, lanosterol, cycloartenol, amyrin, lupeol, and isomultiflorenol. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AII65137.1 | 2.87e-160 | 22 | 522 | 31 | 535 |
| QJR56764.1 | 2.87e-160 | 22 | 522 | 31 | 535 |
| QJR58440.1 | 2.87e-160 | 22 | 522 | 31 | 535 |
| AII67882.1 | 2.87e-160 | 22 | 522 | 31 | 535 |
| AND19555.1 | 2.87e-160 | 22 | 522 | 31 | 535 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1R76_A | 5.62e-17 | 95 | 307 | 77 | 304 | ChainA, pectate lyase [Niveispirillum irakense] |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
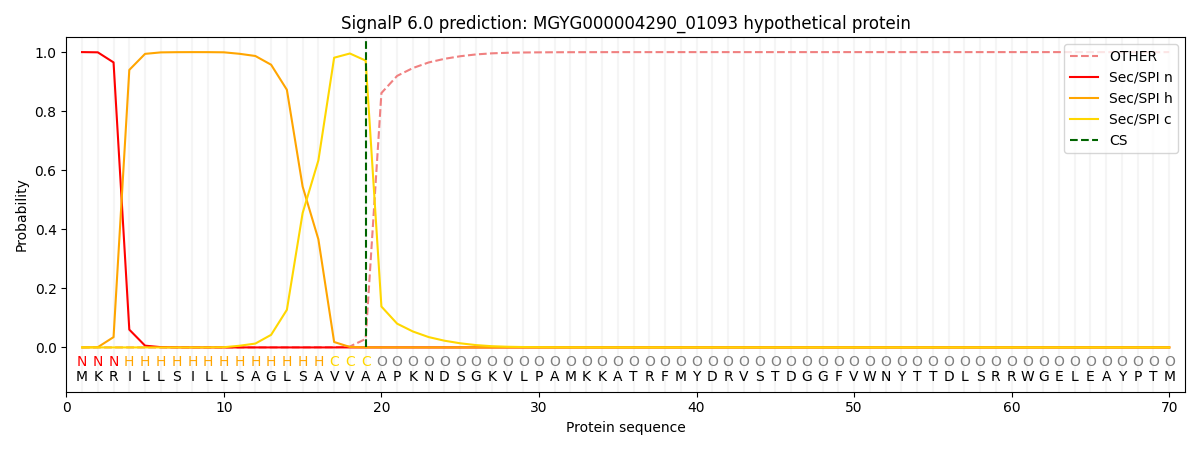
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000484 | 0.998577 | 0.000328 | 0.000222 | 0.000195 | 0.000167 |
