You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004824_01738
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004824_01738
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Bacteroidota; Bacteroidia; Bacteroidales; Bacteroidaceae; Paraprevotella; | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004824_01738 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | CBM67 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 10876; End: 13095 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH78 | 273 | 700 | 4.3e-80 | 0.8690476190476191 |
| CBM67 | 27 | 192 | 1.3e-26 | 0.9034090909090909 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfam17389 | Bac_rhamnosid6H | 5.85e-31 | 314 | 640 | 1 | 340 | Bacterial alpha-L-rhamnosidase 6 hairpin glycosidase domain. This family consists of bacterial rhamnosidase A and B enzymes. L-Rhamnose is abundant in biomass as a common constituent of glycolipids and glycosides, such as plant pigments, pectic polysaccharides, gums or biosurfactants. Some rhamnosides are important bioactive compounds. For example, terpenyl glycosides, the glycosidic precursor of aromatic terpenoids, act as important flavouring substances in grapes. Other rhamnosides act as cytotoxic rhamnosylated terpenoids, as signal substances in plants or play a role in the antigenicity of pathogenic bacteria. |
| pfam08531 | Bac_rhamnosid_N | 1.10e-06 | 47 | 208 | 3 | 166 | Alpha-L-rhamnosidase N-terminal domain. This family consists of bacterial rhamnosidase A and B enzymes. This domain is probably involved in substrate recognition. |
| pfam04685 | DUF608 | 0.007 | 311 | 527 | 17 | 216 | Glycosyl-hydrolase family 116, catalytic region. This represents a family of archaeal, bacterial and eukaryotic glycosyl hydrolases, that belong to superfamily GH116. The primary catabolic pathway for glucosylceramide is catalysis by the lysosomal enzyme glucocerebrosidase. In higher eukaryotes, glucosylceramide is the precursor of glycosphingolipids, a complex group of ubiquitous membrane lipids. Mutations in the human protein cause motor-neurone defects in hereditary spastic paraplegia. The catalytic nucleophile, identified in UniProtKB:Q97YG8_SULSO, is a glutamine-335, with the likely acid/base at Asp-442 and the aspartates at Asp-406 and Asp-458 residues also playing a role in the catalysis of glucosides and xylosides that are beta-bound to hydrophobic groups. The family is defined as GH116, which presently includes enzymes with beta-glucosidase, EC:3.2.1.21, beta-xylosidase, EC:3.2.1.37, and glucocerebrosidase EC:3.2.1.45 activity. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QNL36670.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 735 | 4 | 739 |
| QDH54696.1 | 0.0 | 1 | 735 | 4 | 739 |
| QLG44645.1 | 1.07e-253 | 22 | 734 | 29 | 747 |
| BCI61942.1 | 3.63e-236 | 5 | 732 | 11 | 764 |
| AWX43700.1 | 6.80e-236 | 34 | 714 | 51 | 739 |
Swiss-Prot Hits help
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
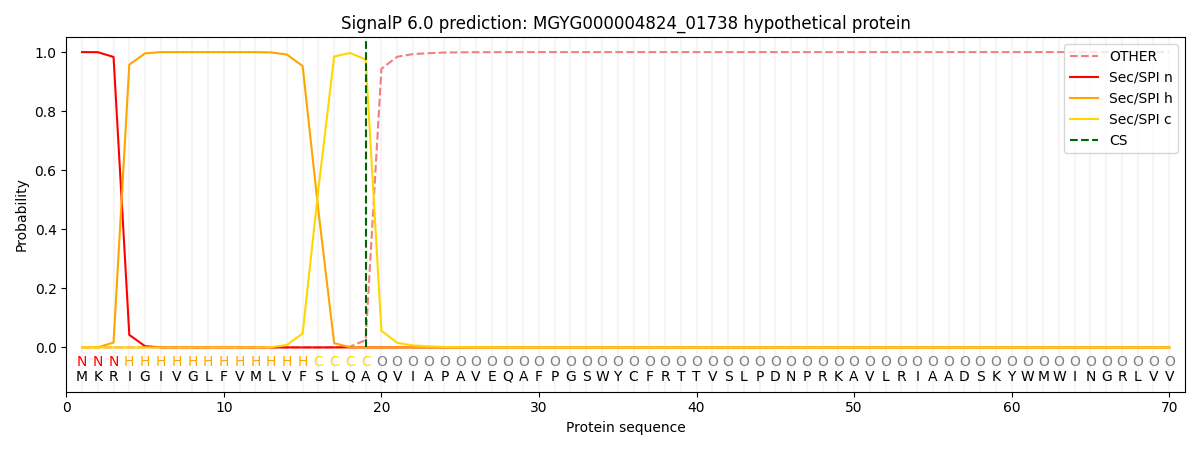
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000347 | 0.998955 | 0.000168 | 0.000183 | 0.000172 | 0.000159 |
