You are browsing environment: HUMAN GUT
CAZyme Information: MGYG000004854_00640
You are here: Home > Sequence: MGYG000004854_00640
Basic Information |
Genomic context |
Full Sequence |
Enzyme annotations |
CAZy signature domains |
CDD domains |
CAZyme hits |
PDB hits |
Swiss-Prot hits |
SignalP and Lipop annotations |
TMHMM annotations
Basic Information help
| Species | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lineage | Bacteria; Firmicutes_A; Clostridia; Oscillospirales; Ruminococcaceae; Ruminococcus; | |||||||||||
| CAZyme ID | MGYG000004854_00640 | |||||||||||
| CAZy Family | GH11 | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Description | hypothetical protein | |||||||||||
| CAZyme Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Genome Property |
|
|||||||||||
| Gene Location | Start: 195106; End: 197292 Strand: - | |||||||||||
CAZyme Signature Domains help
| Family | Start | End | Evalue | family coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GH11 | 54 | 248 | 2.4e-55 | 0.9887005649717514 |
| CBM22 | 281 | 408 | 6.2e-33 | 0.9694656488549618 |
| CE4 | 517 | 633 | 1.2e-21 | 0.8307692307692308 |
CDD Domains download full data without filtering help
| Cdd ID | Domain | E-Value | qStart | qEnd | sStart | sEnd | Domain Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cd10954 | CE4_CtAXE_like | 2.99e-67 | 520 | 710 | 1 | 180 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of Clostridium thermocellum acetylxylan esterase and its bacterial homologs. This family is represented by Clostridium thermocellum acetylxylan esterase (CtAXE, EC 3.1.1.72), a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. CtAXE deacetylates O-acetylated xylan, a key component of plant cell walls. It shows no detectable activity on generic esterase substrates including para-nitrophenyl acetate. It is specific for sugar-based substrates and will precipitate acetylxylan, as a consequence of deacetylation. CtAXE is a monomeric protein containing a catalytic NodB homology domain with the same overall topology and a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold as other CE4 esterases. However, due to differences in the topography of the substrate-binding groove, the chemistry of the active center, and metal ion coordination, CtAXE has different metal ion preference and lacks activity on N-acetyl substrates. It is significantly activated by Co2+. Moreover, CtAXE displays distinctly different ligand coordination to the metal ion, utilizing an aspartate, a histidine, and four water molecules, as opposed to the conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad of other CE4 esterases. |
| pfam00457 | Glyco_hydro_11 | 5.60e-47 | 54 | 247 | 1 | 175 | Glycosyl hydrolases family 11. |
| cd10917 | CE4_NodB_like_6s_7s | 2.26e-44 | 520 | 698 | 1 | 171 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of rhizobial NodB-like proteins. This family belongs to the large and functionally diverse carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily, whose members show strong sequence similarity with some variability due to their distinct carbohydrate substrates. It includes many rhizobial NodB chitooligosaccharide N-deacetylase (EC 3.5.1.-)-like proteins, mainly from bacteria and eukaryotes, such as chitin deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.41), bacterial peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.-), and acetylxylan esterases (EC 3.1.1.72), which catalyze the N- or O-deacetylation of substrates such as acetylated chitin, peptidoglycan, and acetylated xylan. All members of this family contain a catalytic NodB homology domain with the same overall topology and a deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold with 6- or 7 strands. Their catalytic activity is dependent on the presence of a divalent cation, preferably cobalt or zinc, and they employ a conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad closely associated with the conserved catalytic base (aspartic acid) and acid (histidine) to carry out acid/base catalysis. Several family members show diversity both in metal ion specificities and in the residues that coordinate the metal. |
| cd10947 | CE4_SpPgdA_BsYjeA_like | 2.44e-36 | 522 | 707 | 3 | 177 | Catalytic NodB homology domain of Streptococcus pneumoniae peptidoglycan deacetylase PgdA, Bacillus subtilis BsYjeA protein, and their bacterial homologs. This family is represented by Streptococcus pneumoniae peptidoglycan GlcNAc deacetylase (SpPgdA), a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. SpPgdA protects gram-positive bacterial cell wall from host lysozymes by deacetylating peptidoglycan N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) residues. It consists of three separate domains: N-terminal, middle and C-terminal (catalytic) domains. The catalytic NodB homology domain is similar to the deformed (beta/alpha)8 barrel fold adopted by other CE4 esterases, which harbors a mononuclear metalloenzyme employing a conserved His-His-Asp zinc-binding triad closely associated with conserved catalytic base (aspartic acid) and acid (histidine) to carry out acid/base catalysis. The enzyme is able to accept GlcNAc3 as a substrate, with the N-acetyl of the middle sugar being removed by the enzyme. This family also includes Bacillus subtilis BsYjeA protein encoded by the yjeA gene, which is one of the six polysaccharide deacetylase gene homologs (pdaA, pdaB/ybaN, yheN, yjeA, yxkH and ylxY) in the Bacillus subtilis genome. Although homology comparison shows that the BsYjeA protein contains a polysaccharide deacetylase domain, and was predicted to be a membrane-bound xylanase or a membrane-bound chitooligosaccharide deacetylase, more recent research indicates BsYjeA might be a novel non-specific secretory endonuclease which creates random nicks progressively on the two strands of dsDNA, resulting in highly distinguishable intermediates/products very different in chemical and physical compositions over time. In addition, BsYjeA shares several enzymatic properties with the well-understood DNase I endonuclease. Both enzymes are active on ssDNA and dsDNA, both generate random nicks, and both require Mg2+ or Mn2+ for hydrolytic activity. |
| cd10950 | CE4_BsYlxY_like | 2.72e-34 | 516 | 711 | 2 | 188 | Putative catalytic NodB homology domain of uncharacterized protein YlxY from Bacillus subtilis and its bacterial homologs. The Bacillus subtilis genome contains six polysaccharide deacetylase gene homologs: pdaA, pdaB (previously known as ybaN), yheN, yjeA, yxkH and ylxY. This family is represented by Bacillus subtilis putative polysaccharide deacetylase BsYlxY, encoded by the ylxY gene, which is a member of the carbohydrate esterase 4 (CE4) superfamily. Although its biological function still remains unknown, BsYlxY shows high sequence homology to the catalytic domain of Bacillus subtilis pdaB gene encoding a putative polysaccharide deacetylase (BsPdaB), which is essential for the maintenance of spores after the late stage of sporulation and is highly conserved in spore-forming bacteria. However, disruption of the ylxY gene in B. subtilis did not cause any sporulation defect. Moreover, the Asp residue in the classical His-His-Asp zinc-binding motif of CE4 esterases is mutated to a Val residue in this family. Other catalytically relevant residues of CE4 esterases are also not conserved, which suggest that members of this family may be inactive. |
CAZyme Hits help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBL18305.1 | 7.52e-195 | 1 | 728 | 1 | 883 |
| ADU21434.1 | 1.31e-177 | 1 | 726 | 1 | 778 |
| AEE64769.1 | 3.99e-167 | 1 | 726 | 1 | 755 |
| ADU20638.1 | 2.03e-155 | 50 | 726 | 62 | 678 |
| AAA85198.1 | 2.86e-155 | 50 | 726 | 62 | 678 |
PDB Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2C1F_A | 1.59e-131 | 39 | 262 | 3 | 225 | Thestructure of the family 11 xylanase from Neocallimastix patriciarum [Neocallimastix patriciarum] |
| 2VG9_A | 3.88e-127 | 39 | 255 | 3 | 216 | Crystalstructure of Loop Swap mutant of Necallimastix patriciarum Xyn11A [Neocallimastix patriciarum] |
| 4IXL_A | 4.84e-47 | 30 | 248 | 19 | 227 | Crystalstructure of endo-beta-1,4-xylanase from the alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. SN5 [Bacillus sp. (in: Bacteria)],4IXL_B Crystal structure of endo-beta-1,4-xylanase from the alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. SN5 [Bacillus sp. (in: Bacteria)] |
| 1H4G_A | 1.53e-46 | 51 | 248 | 9 | 194 | Oligosaccharide-bindingto family 11 xylanases: both covalent intermediate and mutant-product complexes display 2,5B conformations at the active-centre [Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens],1H4G_B Oligosaccharide-binding to family 11 xylanases: both covalent intermediate and mutant-product complexes display 2,5B conformations at the active-centre [Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens],1QH6_A CATALYSIS AND SPECIFICITY IN ENZYMATIC GLYCOSIDE HYDROLASES: A 2,5B CONFORMATION FOR THE GLYCOSYL-ENZYME INTERMIDIATE REVEALED BY THE STRUCTURE OF THE BACILLUS AGARADHAERENS FAMILY 11 XYLANASE [Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens],1QH6_B CATALYSIS AND SPECIFICITY IN ENZYMATIC GLYCOSIDE HYDROLASES: A 2,5B CONFORMATION FOR THE GLYCOSYL-ENZYME INTERMIDIATE REVEALED BY THE STRUCTURE OF THE BACILLUS AGARADHAERENS FAMILY 11 XYLANASE [Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens],1QH7_A CATALYSIS AND SPECIFICITY IN ENZYMATIC GLYCOSIDE HYDROLASES: A 2,5B CONFORMATION FOR THE GLYCOSYL-ENZYME INTERMIDIATE REVEALED BY THE STRUCTURE OF THE BACILLUS AGARADHAERENS FAMILY 11 XYLANASE [Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens],1QH7_B CATALYSIS AND SPECIFICITY IN ENZYMATIC GLYCOSIDE HYDROLASES: A 2,5B CONFORMATION FOR THE GLYCOSYL-ENZYME INTERMIDIATE REVEALED BY THE STRUCTURE OF THE BACILLUS AGARADHAERENS FAMILY 11 XYLANASE [Salipaludibacillus agaradhaerens] |
| 2F6B_A | 2.83e-46 | 51 | 248 | 9 | 194 | Structuraland active site modification studies implicate Glu, Trp and Arg in the activity of xylanase from alkalophilic Bacillus sp. (NCL 87-6-10). [Bacillus],2F6B_B Structural and active site modification studies implicate Glu, Trp and Arg in the activity of xylanase from alkalophilic Bacillus sp. (NCL 87-6-10). [Bacillus] |
Swiss-Prot Hits download full data without filtering help
| Hit ID | E-Value | Query Start | Query End | Hit Start | Hit End | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P29127 | 2.85e-128 | 33 | 255 | 25 | 246 | Bifunctional endo-1,4-beta-xylanase A OS=Neocallimastix patriciarum OX=4758 GN=XYNA PE=1 SV=1 |
| Q53317 | 3.60e-85 | 1 | 458 | 1 | 459 | Xylanase/beta-glucanase OS=Ruminococcus flavefaciens OX=1265 GN=xynD PE=3 SV=2 |
| P83513 | 4.17e-59 | 38 | 719 | 11 | 592 | Bifunctional xylanase/deacetylase OS=Pseudobutyrivibrio xylanivorans OX=185007 GN=xyn11A PE=1 SV=2 |
| P17137 | 6.17e-42 | 55 | 253 | 72 | 257 | Endo-1,4-beta-xylanase OS=Clostridium saccharobutylicum OX=169679 GN=xynB PE=3 SV=1 |
| Q8GJ44 | 6.00e-41 | 1 | 253 | 1 | 229 | Endo-1,4-beta-xylanase A OS=Thermoclostridium stercorarium OX=1510 GN=xynA PE=1 SV=2 |
SignalP and Lipop Annotations help
This protein is predicted as SP
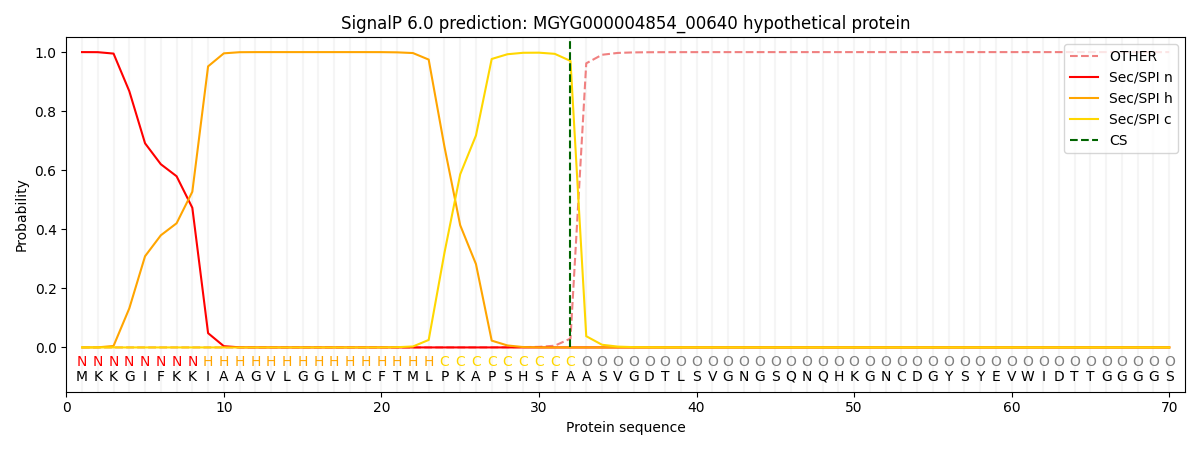
| Other | SP_Sec_SPI | LIPO_Sec_SPII | TAT_Tat_SPI | TATLIP_Sec_SPII | PILIN_Sec_SPIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000237 | 0.999104 | 0.000177 | 0.000175 | 0.000151 | 0.000136 |
